The Derating Factor Calculator helps engineers, electricians, and designers determine the reduced operating capacity of electrical components, cables, and mechanical systems under specific conditions. Derating is crucial in ensuring safety, efficiency, and longevity of equipment by preventing overheating and damage. This tool is widely used in power systems, electronics, and mechanical engineering to calculate the actual safe operating limits of devices.
Formula of Derating Factor Calculator
The Derating Factor is calculated using the following formula:
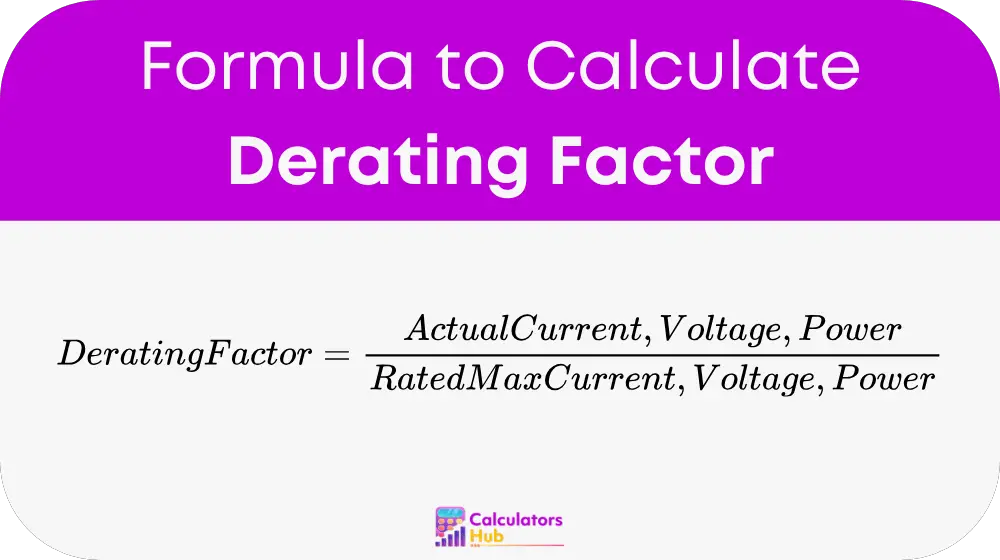
where:
- Actual Operating Condition refers to the real working value of current, voltage, or power under specific environmental conditions.
- Rated Maximum Condition is the manufacturer-specified maximum allowable limit for current, voltage, or power.
This formula ensures that systems operate within safe limits, reducing the risk of failure and enhancing reliability.
Derating Factor Reference Table
This table provides estimated derating factors for different operating conditions to help engineers make quick assessments without manual calculations.
| Component Type | Rated Maximum (A, V, W) | Actual Operating (A, V, W) | Derating Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Cable | 100 A | 80 A | 0.80 |
| Power Supply | 500 W | 400 W | 0.80 |
| Transformer | 250 V | 225 V | 0.90 |
| Motor | 10 A | 7.5 A | 0.75 |
| Resistor | 5 W | 3.5 W | 0.70 |
These values help engineers determine safe operational limits in different applications.
Example of Derating Factor Calculator
An engineer is designing an electrical system and needs to determine if a cable rated at 200 A will be safe when used in an environment where the actual operating current is 150 A.
Using the formula:
Derating Factor = 150 A / 200 A
= 0.75
This means that the cable is operating at 75% of its maximum capacity, ensuring safe performance within acceptable limits.
Most Common FAQs
The derating factor ensures electrical components and mechanical systems operate safely under varying environmental and load conditions, preventing failures and overheating.
Higher temperatures reduce the efficiency of electrical components, requiring a lower operating capacity. Derating factors help adjust for temperature variations to maintain safe operation.
Yes, derating factors are use in mechanical applications such as motor load reductions, heat dissipation, and stress analysis to ensure durability and longevity.