A decoupling capacitor, or bypass capacitor, is an essential component in electronic circuits. It serves to filter out voltage spikes and noise, ensuring stable voltage levels to electronic devices. The decoupling capacitor calculator is a tool designed to simplify the process of selecting the right capacitor for your circuit. It calculates the capacitance value needed to effectively decouple noise from the power supply, based on specific parameters of your circuit.
Formula of Decoupling Capacitor Calculator
The fundamental formula used by the calculator is:
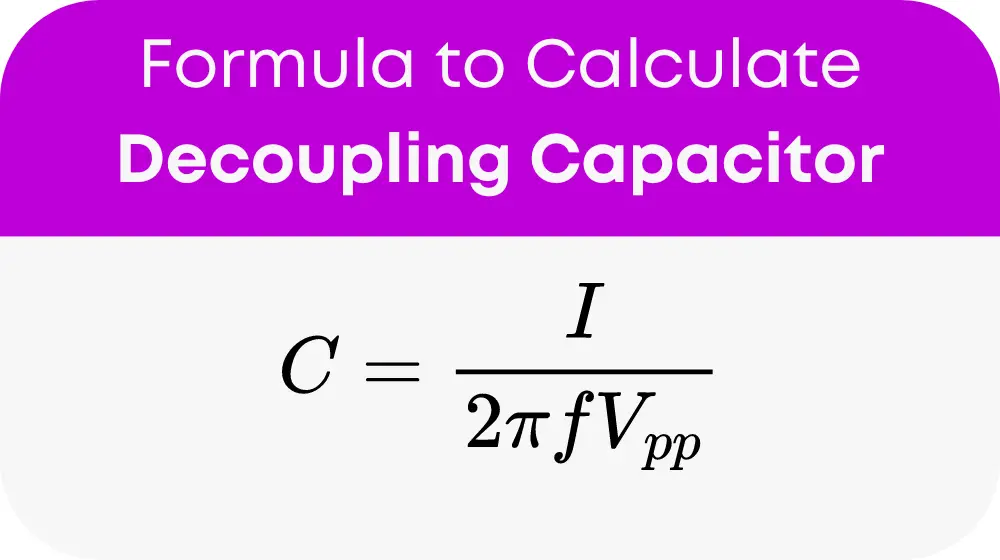
where:
- CC represents the capacitance of the decoupling capacitor (in Farads),
- II is the peak-to-peak ripple current (in Amperes),
- ff is the frequency of the ripple (in Hertz),
- VppVpp is the peak-to-peak ripple voltage (in Volts).
Understanding this formula is key to comprehending how the calculator determines the appropriate capacitor size for your needs.
General Terms Table
To aid in the practical use of the calculator and enhance understanding, the following table provides general terms and their relevance in using the calculator effectively:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Capacitance (C) | The ability of a capacitor to store an electrical charge, measured in Farads. |
| Ripple Current (I) | The AC component of an otherwise DC current, measured in Amperes. |
| Frequency (f) | The rate at which the current alternates, measured in Hertz. |
| Ripple Voltage (Vpp) | The difference in the maximum and minimum values of the ripple, measured in Volts. |
This table serves as a quick reference guide to understand the variables involved in using the decoupling capacitor calculator.
Example of Decoupling Capacitor Calculator
Consider a scenario where you need to determine the capacitance for a decoupling capacitor. Assume the peak-to-peak ripple current is 0.5 Amperes, the frequency of the ripple is 1 MHz (1,000,000 Hertz), and the peak-to-peak ripple voltage is 0.1 Volts. Using the formula:
C = 0.5 / 2π × 1,000,000 × 0.1 = 7.96×10−7 Farads
or approximately 796 nF (nanofarads). This example demonstrates how to use the formula to calculate the needed capacitance value.
Most Common FAQs
A1: A decoupling capacitor is crucial because it helps stabilize the voltage supply to electronic components, filtering out noise and preventing potential interference that could disrupt the circuit’s operation.
A2: While various capacitors can serve as decoupling capacitors, it’s essential to choose one with a suitable capacitance value for your specific circuit requirements. Factors such as the capacitor’s ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) and ESL (Equivalent Series Inductance) also play a critical role.
A3: Ideally, place the decoupling capacitor as close as possible to the power supply pin of the component it is intended to protect. This positioning minimizes the loop area and effectively filters out unwanted noise and voltage spikes.