This tool simplifies the process of determining the optimal wire gauge needed for DC electrical circuits. By considering factors such as current, wire length, material, and desired voltage drop, the calculator provides accurate and reliable sizing recommendations.
Formula of DC Current Wire Size Calculator
To calculate the correct wire size, use the following formula:
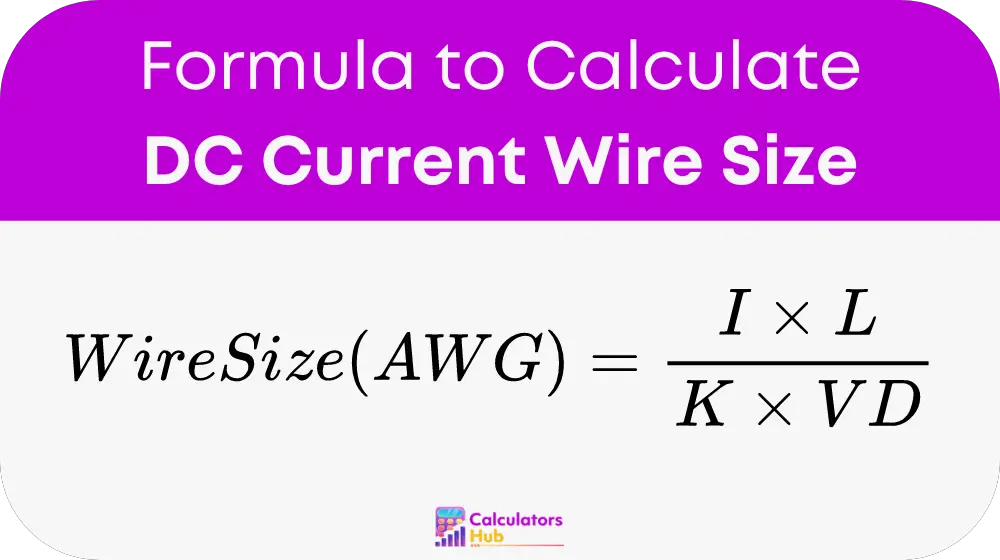
- I represents the current in amperes.
- L is the total length of the wire in feet.
- K stands for a constant, typically 12.9 for copper and 21.2 for aluminum.
- VD is the voltage drop in volts.
Steps to Use the Formula
Follow these steps to determine the appropriate wire size:
- Identify Current (I): Determine the amount of current that will flow through the wire.
- Measure Wire Length (L): Calculate the total length of the wire run.
- Choose the Constant (K): Select the constant based on the wire material (copper or aluminum).
- Define Voltage Drop (VD): Decide the maximum acceptable voltage drop.
- Calculate Wire Size: Use the formula to find the correct wire gauge.
Reference Table
Here is a quick reference table for commonly used wire sizes based on different currents and lengths for both copper and aluminum:
| Current (A) | Length (ft) | Copper Wire Size (AWG) | Aluminum Wire Size (AWG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 50 | 16 | 14 |
| 20 | 50 | 14 | 12 |
| 30 | 50 | 12 | 10 |
Example of DC Current Wire Size Calculator
Consider a scenario where you need to install a wire that will carry 20 amperes over a distance of 100 feet using copper. The acceptable voltage drop is 3 volts. Using the formula:
Wire Size (AWG) = (20 * 100) / (12.9 * 3) ≈ 51.36
This calculation suggests using a wire gauge slightly larger than 51 AWG; however, since AWG sizes are standardized, you would round to the nearest available size.
Most Common FAQs
The longer the wire, the larger the wire size needed to compensate for increased resistance and voltage drop.
Copper, having a lower resistance than aluminum, generally requires a smaller wire size for the same application.
Incorrect wire sizing can lead to excessive voltage drops, increased resistance, overheating, and potential fire hazards.