The Current Per Phase Calculator helps determine the current flowing through each phase in a three-phase electrical system. This calculation is essential in electrical engineering and power distribution to ensure circuits and equipment operate within safe limits.
In three-phase power systems, electrical loads are distributed across multiple phases, improving efficiency and reducing losses. Knowing the current per phase is necessary for sizing circuit breakers, designing electrical panels, and preventing system overloads.
This calculator is commonly used by electrical engineers, technicians, and industrial facility managers to ensure optimal power distribution in motors, transformers, and power networks.
Formula of Current Per Phase Calculator
To calculate current per phase in a three-phase system, use the following formula:
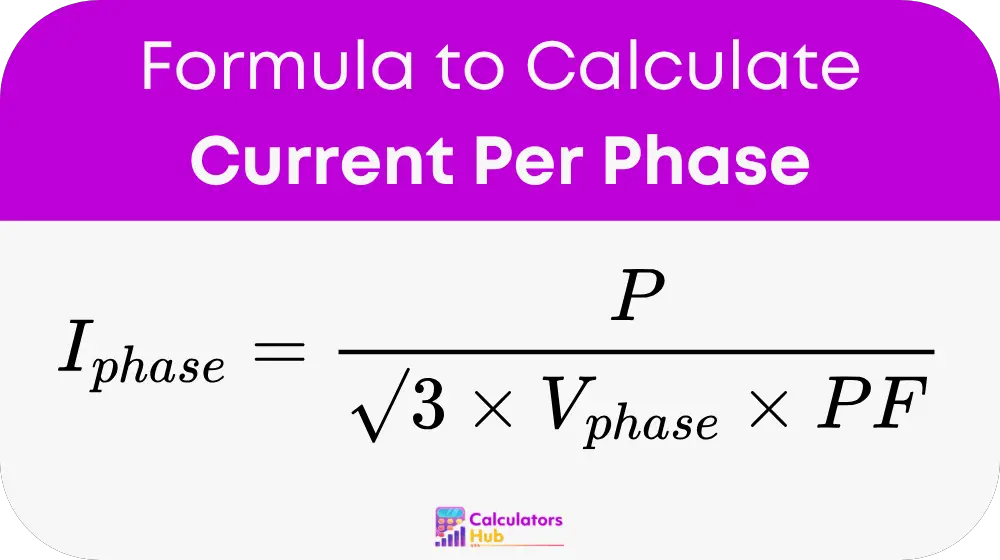
Where:
- I_phase = Current per phase (in amperes, A)
- P = Total power (in watts, W)
- V_phase = Phase voltage (in volts, V)
- PF = Power factor (a number between 0 and 1, representing the efficiency of power usage)
- √3 = A constant, approximately 1.732, used for three-phase systems
This formula provides an accurate estimation of the current flowing through each phase based on total power, voltage, and power factor.
General Current Per Phase Reference Table
To simplify calculations, the table below provides pre-calculated current per phase values for common power ratings and voltage levels.
| Total Power (W) | Phase Voltage (V) | Power Factor (PF) | Current Per Phase (A) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10,000 | 230 | 0.8 | 31.33 |
| 20,000 | 400 | 0.9 | 32.08 |
| 30,000 | 415 | 0.85 | 41.01 |
| 50,000 | 440 | 0.95 | 61.37 |
| 75,000 | 480 | 0.9 | 100.38 |
This table provides a quick estimate for different power and voltage levels without manual calculation.
Example of Current Per Phase Calculator
Suppose an industrial motor operates at a total power of 20,000W, with a phase voltage of 400V, and a power factor of 0.9.
Using the formula:
I_phase = 20,000 / (√3 × 400 × 0.9)
I_phase = 20,000 / 623.52 ≈ 32.08A
This means that each phase of the system carries approximately 32.08A.
Most Common FAQs
Determining current per phase ensures that electrical systems are design safely and efficiently. It helps prevent overloading, reduces energy losses, and ensures compliance with electrical standards.
The power factor represents how effectively electrical power is use. A lower power factor means more current is require to deliver the same amount of power, increasing system losses and costs.
No, this formula is specifically for three-phase systems. Single-phase systems use a simpler formula: I = P / (V × PF).