The Current Limiting Resistance Calculator helps determine the appropriate resistor value needed to restrict current flow in an electrical circuit. It is commonly used to protect sensitive components, such as LEDs, transistors, and integrated circuits, from excessive current that could cause overheating or permanent damage.
This calculator is essential for electronics engineers, hobbyists, and technicians who need to design circuits that operate within safe current limits. By entering the supply voltage, component voltage drop, and the maximum current allowed, users can quickly calculate the correct resistor value to prevent overcurrent issues.
Formula of Current Limiting Resistance Calculator
The formula to calculate the current-limiting resistance is:
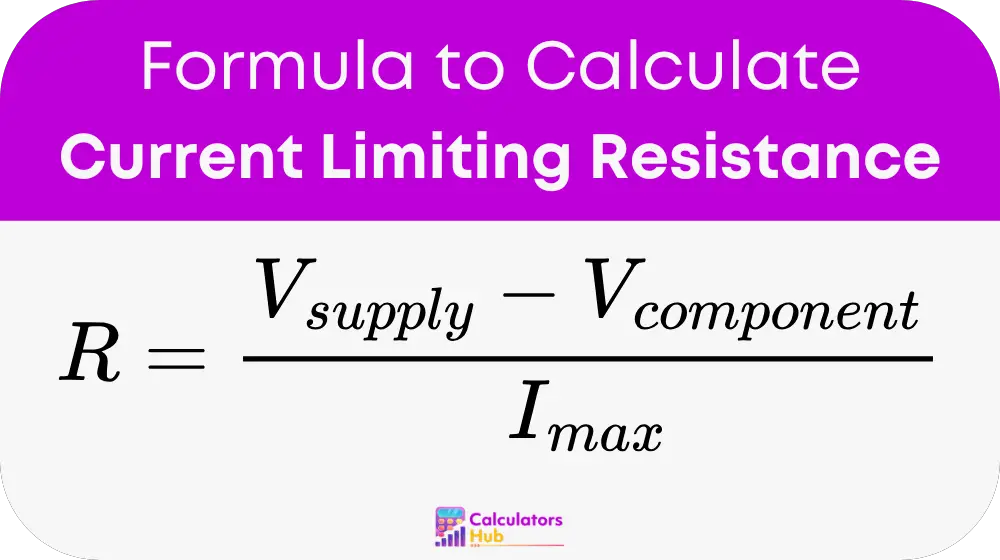
Where:
- R = Current-limiting resistance (in ohms, Ω).
- V_supply = Supply voltage (in volts, V).
- V_component = Voltage drop across the component (in volts, V).
- I_max = Maximum current allowed through the component (in amperes, A).
This formula ensures that the selected resistor limits the current flow to a safe level, preventing component failure and optimizing circuit performance.
General Current Limiting Resistor Table
To make calculations easier, the table below provides pre-calculated resistor values for common voltage and current combinations.
| Supply Voltage (V) | Component Voltage Drop (V) | Max Current (A) | Required Resistor (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 2 | 0.02 | 150 |
| 9 | 3 | 0.02 | 300 |
| 12 | 2 | 0.03 | 333 |
| 24 | 5 | 0.05 | 380 |
| 48 | 10 | 0.1 | 380 |
This table provides a quick reference for selecting resistor values in various circuit applications.
Example of Current Limiting Resistance Calculator
Suppose a circuit designer is working with an LED that has a voltage drop of 2V, a supply voltage of 9V, and a maximum allowable current of 20mA (0.02A). Using the formula:
R = (9 – 2) / 0.02
R = 7 / 0.02 = 350Ω
This means a 350-ohm resistor should be used to limit the current safely.
Most Common FAQs
A current-limiting resistor prevents excessive current from flowing through a component, protecting it from damage. It is widely used in LED circuits, transistor circuits, and power supply designs.
To determine the appropriate resistor wattage, calculate the power dissipation using P = I² × R. Selecting a resistor with at least double the required wattage ensures reliability and prevents overheating.
Yes, using a slightly higher resistor value further limits current flow, which can extend the lifespan of the component. However, using an excessively high resistor value may reduce current too much, affecting circuit performance.