—
The Current Capacity Calculator helps determine the maximum current a wire can safely carry based on its material, cross-sectional area, voltage, and length. This calculation is crucial for electrical engineers, electricians, and professionals working with electrical circuits to prevent overheating, voltage drops, and electrical failures.
Wires carrying excessive current can overheat, leading to damage, energy losses, or even fires. By using this calculator, users can ensure they select the right wire size for a given electrical load, improving safety and efficiency.
Formula of Current Capacity Calculator
The current capacity of a wire is calculated using the following formula:
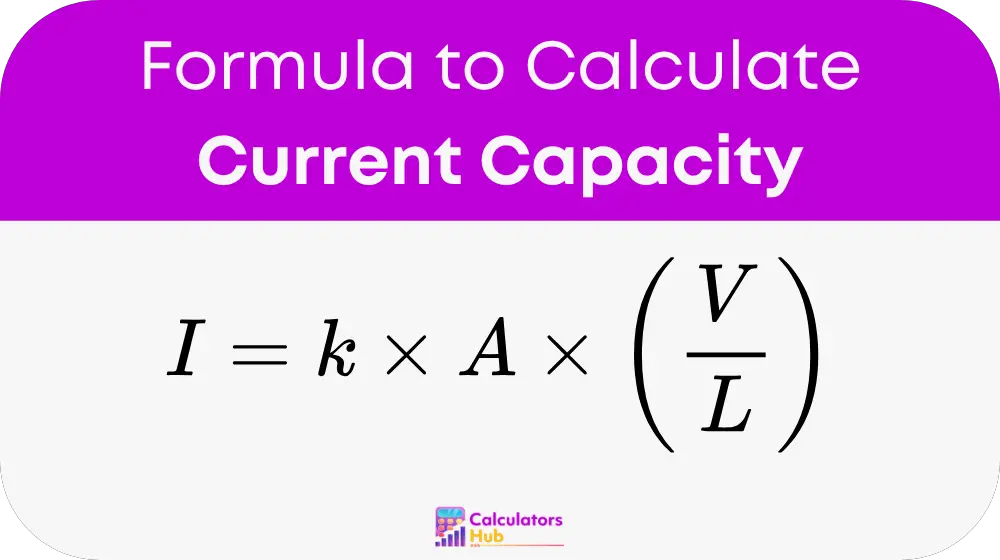
Where:
- I = Current (in Amps)
- k = Material constant (varies based on the conductor material, such as copper or aluminum)
- A = Cross-sectional area of the wire (in square meters or square inches)
- V = Voltage (in Volts)
- L = Length of the wire (in meters or feet)
This formula helps estimate the amount of current a wire can safely carry without significant energy losses or safety risks.
General Wire Current Capacity Table
The table below provides approximate values of current-carrying capacity for common wire sizes and materials.
| Wire Material | Cross-Sectional Area (mm²) | Voltage (V) | Max Current Capacity (Amps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | 1.5 | 230 | 15 |
| Copper | 2.5 | 230 | 20 |
| Copper | 4.0 | 230 | 25 |
| Copper | 6.0 | 230 | 32 |
| Aluminum | 10.0 | 230 | 40 |
| Aluminum | 16.0 | 230 | 50 |
This table provides a quick reference to help users select appropriate wire sizes for their electrical applications.
Example of Current Capacity Calculator
Suppose an electrician needs to determine the current capacity of a copper wire with a cross-sectional area of 4 mm², a voltage of 230V, and a wire length of 20 meters. Given that the material constant (k) for copper is approximately 0.017, the formula is applied as follows:
I = 0.017 × 4 × (230 / 20)
I = 0.017 × 4 × 11.5 = 0.782 Amps
This means that under these conditions, the wire can safely carry approximately 0.78 Amps without significant voltage drop or overheating.
Most Common FAQs
Different materials have different electrical conductivities, which affect their ability to carry current. Copper has a higher conductivity than aluminum, meaning it can carry more current with less resistance.
Longer wires have more resistance, which leads to voltage drops and heat generation. Using a thicker wire can help reduce these issues in long-distance electrical installations.
If a wire carries more current than its rated capacity, it may overheat, leading to insulation damage, energy loss, or even fire hazards. Ensuring the correct wire size prevents these risks and maintains electrical safety.