The Cockroft Walton Multiplier Calculator is a specialized tool used to compute the output voltage of a Cockroft-Walton voltage multiplier circuit. This circuit converts low AC input voltage into a significantly higher DC output voltage through a series of capacitors and diodes arranged in multiple stages. It is widely used in applications like particle accelerators, X-ray machines, and high-voltage power supplies.
This calculator simplifies the complex process of calculating the circuit’s output voltage, considering factors like the number of stages, load current, input frequency, and component values.
Formula of Cockroft Walton Multiplier Calculator
The output voltage of a Cockroft-Walton multiplier can be calculated using the following formula:
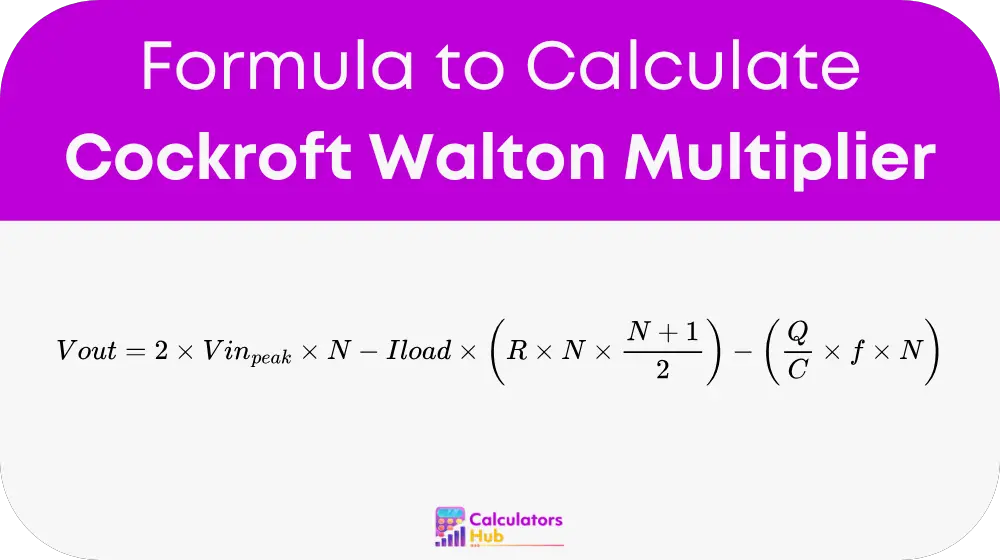
Where:
- Vout: Output voltage
- Vin_peak: Peak input voltage of the AC supply
- N: Number of stages in the multiplier
- Iload: Load current
- R: Equivalent series resistance of the diodes and capacitors
- Q: Charge transferred in each cycle
- C: Capacitance of each capacitor
- f: Input AC frequency
Explanation
- 2 × Vin_peak × N: Represents the ideal voltage gain, assuming no losses.
- Iload × (R × N × (N + 1) / 2): Accounts for voltage drop due to the load current and internal resistance.
- (Q / C × f × N): Accounts for ripple voltage and voltage drop caused by charge storage limitations.
This formula ensures accurate output voltage predictions, factoring in real-world inefficiencies.
Reference Table for Quick Use
Here’s a reference table showcasing approximate output voltages for a standard Cockroft-Walton multiplier with typical parameters. These are general estimates to help users without requiring detailed calculations.
| Input AC Voltage (V_peak) | Number of Stages (N) | Capacitance (µF) | Load Current (mA) | Output Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 5 | 1 | 10 | 920 |
| 120 | 6 | 0.5 | 15 | 1080 |
| 200 | 8 | 0.1 | 5 | 1600 |
| 300 | 10 | 0.05 | 2 | 2800 |
This table assumes minimal resistance and ripple. Actual results may vary based on circuit parameters.
Example of Cockroft Walton Multiplier Calculator
Let’s calculate the output voltage of a Cockroft-Walton multiplier with the following specifications:
- Vin_peak: 120 V
- N: 6 stages
- Iload: 15 mA
- R: 5 Ω
- C: 0.5 µF
- f: 50 Hz
- Q: 0.015 C (calculated as Iload / f)
Step 1: Ideal Voltage
Ideal voltage gain = 2 × Vin_peak × N = 2 × 120 × 6 = 1440 V
Step 2: Voltage Drop Due to Load
Voltage drop due to load = Iload × (R × N × (N + 1) / 2) = 0.015 × (5 × 6 × (6 + 1) / 2) = 0.015 × 105 = 1.575 V
Step 3: Ripple Voltage
Ripple voltage = Q / (C × f × N) = 0.015 / (0.5 × 10⁻⁶ × 50 × 6) = 0.015 / 0.00015 = 100 V
Step 4: Final Output Voltage
Vout = Ideal voltage gain − Voltage drop − Ripple voltage = 1440 − 1.575 − 100 ≈ 1338.425 V
The output voltage is approximately 1338.4 V.
Most Common FAQs
The main limitations include significant voltage drops due to load current, increased ripple voltage with more stages, and reduced efficiency at higher output voltages. These factors should be considered during design and implementation.
Increasing the capacitance or input frequency can reduce ripple voltage. However, this may require higher-quality components, which could increase costs.
The practical number of stages depends on the desired output voltage, input frequency, and load requirements. Too many stages can lead to excessive losses and unstable performance.