A capacitor power calculator is a tool used to calculate the reactive power associated with a capacitor in an AC (alternating current) circuit. Capacitors in AC circuits store and release energy, leading to reactive power, which is different from real power. While real power does work in the circuit, reactive power represents energy being stored and returned, particularly in capacitive or inductive components.
Understanding the power drawn by capacitors in AC circuits is essential for designing power distribution systems, motor controllers, and various other electrical devices. By using the capacitor power calculator, you can easily determine how much reactive power is being produced by a capacitor based on its capacitance, the voltage applied, and the AC signal's frequency.
This information helps with energy management, improving the power factor in industrial applications, and ensuring that electrical systems operate efficiently.
Formula of Capacitor Power Calculator
The power associated with a capacitor can be calculated using the following formula:
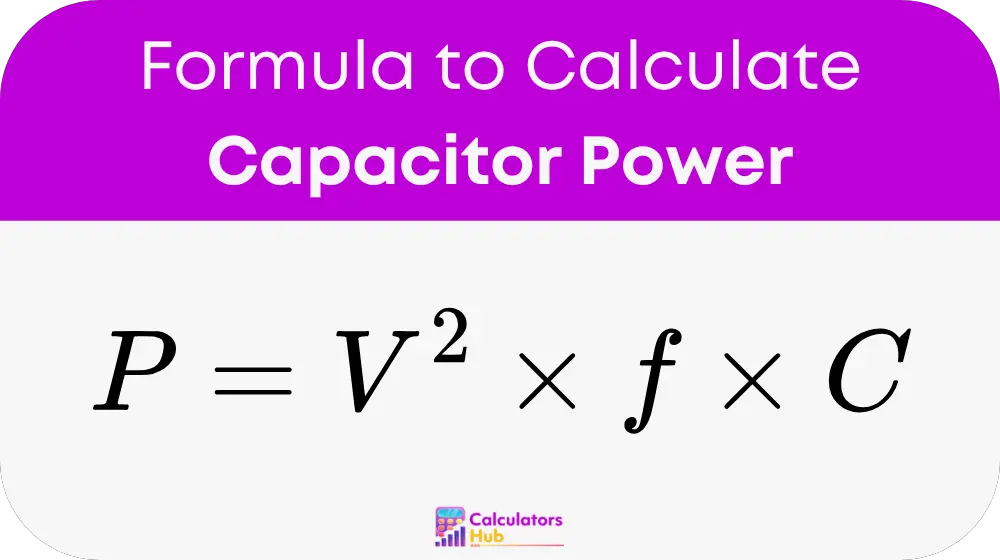
Where:
- P = Reactive power (in volt-amperes reactive, or VAR)
- V = Voltage across the capacitor (in volts)
- f = Frequency of the AC signal (in hertz)
- C = Capacitance (in farads)
This formula helps in understanding how capacitive power changes with respect to frequency, voltage, and capacitance. In general, the power output increases with higher voltage, capacitance, or frequency.
Common Terms and Quick Lookup Table
To assist users in quickly finding relevant values, here’s a table that shows how power varies across different capacitor values and typical AC frequencies. These values are calculated based on a fixed voltage of 230V, which is a common standard voltage in many regions.
| Capacitance (µF) | Frequency (Hz) | Reactive Power (VAR) at 230V |
|---|---|---|
| 1 µF | 50 Hz | 2.65 VAR |
| 10 µF | 50 Hz | 26.5 VAR |
| 100 µF | 50 Hz | 265 VAR |
| 1 µF | 60 Hz | 3.18 VAR |
| 10 µF | 60 Hz | 31.8 VAR |
| 100 µF | 60 Hz | 318 VAR |
| 1 µF | 400 Hz | 21.2 VAR |
| 10 µF | 400 Hz | 212 VAR |
| 100 µF | 400 Hz | 2120 VAR |
This table demonstrates the typical range of reactive power values based on capacitance and frequency. By referencing this table, you can estimate the power without needing to do the calculation each time. This quick lookup is particularly useful for engineers working with different capacitive components across varying frequencies.
Example of Capacitor Power Calculator
Problem:
You are designing a power system with a capacitor that has a capacitance of 47 µF. The system runs on an AC signal with a frequency of 50 Hz, and the voltage applied across the capacitor is 230V. You want to calculate the reactive power of this capacitor.
Solution:
- Convert the capacitance to farads:
- C = 47 * 10^-6 F = 0.000047 F
- Voltage V = 230V
- Frequency f = 50 Hz
- Apply the formula:
- P = V^2 * f * C
- P = (230)^2 * 50 * 0.000047
- P = 52900 * 50 * 0.000047
- P ≈ 124.2 VAR
Answer:
The reactive power for the capacitor in this system is approximately 124.2 VAR.
Most Common FAQs
Reactive power is the power consume by reactive components (such as capacitors and inductors) in an AC circuit, which stores and releases energy but doesn’t do any real work. It is important because it affects the overall efficiency of power systems and influences the power factor, which measures how effectively electrical power is being used.
Capacitors themselves do not directly reduce energy consumption, but they can improve the power factor of a system. By compensating for reactive power, capacitors reduce the apparent power drawn from the supply, thereby improving system efficiency and potentially reducing energy costs in large industrial settings.
The power associated with a capacitor increases with higher capacitance and higher AC frequency. This is because capacitors store more energy at higher frequencies and when their capacitance is larger. As a result, systems operating at higher frequencies or with larger capacitors will exhibit greater reactive power.