A Cable Inductance Per Meter Calculator is a specialized tool designed to calculate the inductance of a cable or wire per unit length (usually in meters). Inductance is a property of electrical conductors that causes opposition to changes in current flow. It’s especially important in high-frequency applications, such as radio frequency transmission lines, and in power systems. The calculator uses the physical dimensions of the cable and the relative positions of conductors to determine the inductance.
The inductance per meter can help engineers and electricians understand how the cable will perform in different electrical systems. Higher inductance values can lead to more energy storage in the magnetic field, which affects how signals or power is transmitted. This is crucial when designing circuits for data transmission, communication systems, and power distribution.
Formula of Cable Inductance Per Meter Calculator
The formula to calculate inductance per meter of a cable is as follows:
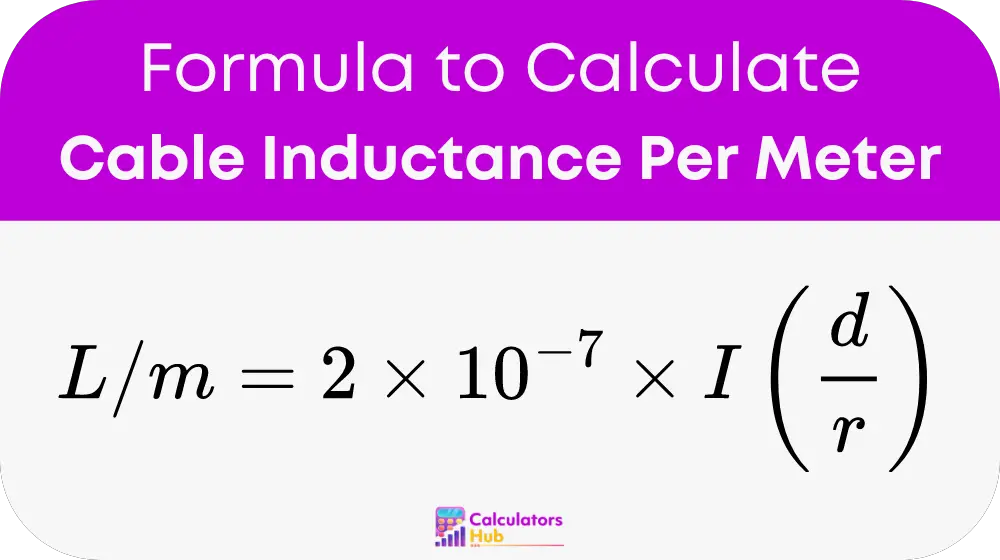
Where:
- d is the distance between the centers of the two conductors (in meters).
- r is the radius of the conductor (in meters).
- ln is the natural logarithm.
This formula is based on the assumption of two parallel conductors and is often used in electrical engineering to estimate the inductance of cables or wires. It helps in determining how the layout and size of conductors affect inductive behavior.
Explanation of Terms
- Inductance (L): The measure of the conductor's ability to store electrical energy in the form of a magnetic field.
- Distance between conductors (d): This refers to the physical distance between the centers of two conductors. A larger distance results in lower inductance.
- Radius of the conductor (r): The cross-sectional radius of the conductor. A smaller radius leads to higher inductance.
- Natural Logarithm (ln): A mathematical function used to relate the ratio of d to r.
Helpful Table for Common Terms
Below is a table that lists typical distances (d) between conductors and the resulting inductance per meter (L) for a common range of wire sizes (radius, r). This table provides quick reference values, so users don't need to calculate each time.
| Distance Between Conductors (d) | Radius of Conductor (r) | Inductance (L) Per Meter (μH) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 m | 0.001 m | 0.138 μH |
| 0.02 m | 0.001 m | 0.231 μH |
| 0.05 m | 0.002 m | 0.370 μH |
| 0.10 m | 0.005 m | 0.607 μH |
| 0.20 m | 0.005 m | 0.916 μH |
This table provides some general inductance values based on different physical configurations. Users can refer to this table without needing to manually perform calculations, making the process much faster for designing circuits or making quick estimations.
Example of Cable Inductance Per Meter Calculator
Let’s work through an example to understand how the Cable Inductance Per Meter Calculator functions.
Problem: We have two parallel conductors that are spaced 0.03 meters apart, and each conductor has a radius of 0.002 meters. Using the formula, we need to find the inductance per meter of the cable.
Solution:
Using the formula: Inductance (L) per meter = (2 × 10^(-7)) × ln(d / r)
- d = 0.03 meters (distance between centers of the conductors)
- r = 0.002 meters (radius of each conductor)
- ln(0.03 / 0.002) = ln(15) ≈ 2.708
Now, calculate the inductance: L = (2 × 10^(-7)) × 2.708 L ≈ 5.416 × 10^(-7) H/m
Thus, the inductance per meter is approximately 0.5416 μH/m.
Most Common FAQs
Inductance is crucial because it impacts how electrical signals travel through a conductor. In high-frequency systems, such as data transmission or radio frequency applications, higher inductance can lead to signal distortion or energy loss. Understanding the inductance per meter of a cable helps in designing efficient circuits that minimize these effects.
The distance between conductors (d) directly affects inductance. As the distance increases, the inductance decreases. This is because inductance is related to the magnetic field that forms around the conductor. A greater separation between the conductors reduces the mutual magnetic interaction, thereby lowering the inductance.
Yes, the Cable Inductance Per Meter Calculator is versatile and can be used for different types of cables, including coaxial, twisted pair, and parallel conductor cables. However, the basic formula assumes parallel conductors. For more complex cable geometries, the calculations might require specific adaptations or additional factors.