The Cable Duct Capacity Calculator helps determine the number of cables that can safely be installed within a cable duct. Cable ducts are essential for organizing and protecting electrical cables in a wide range of environments, including commercial buildings, industrial settings, and residential projects. Choosing the correct duct size ensures the cables have adequate space, preventing overheating, damage, or reduced performance due to overfilling.
The calculator takes into account the internal dimensions of the duct, the fill ratio, and the cross-sectional area of each cable to determine how many cables can fit into the duct. This calculation ensures that the cables are safely housed with enough room for airflow and future maintenance or expansion.
Formula of Cable Duct Capacity Calculator
The formula for calculating the capacity of a cable duct is:
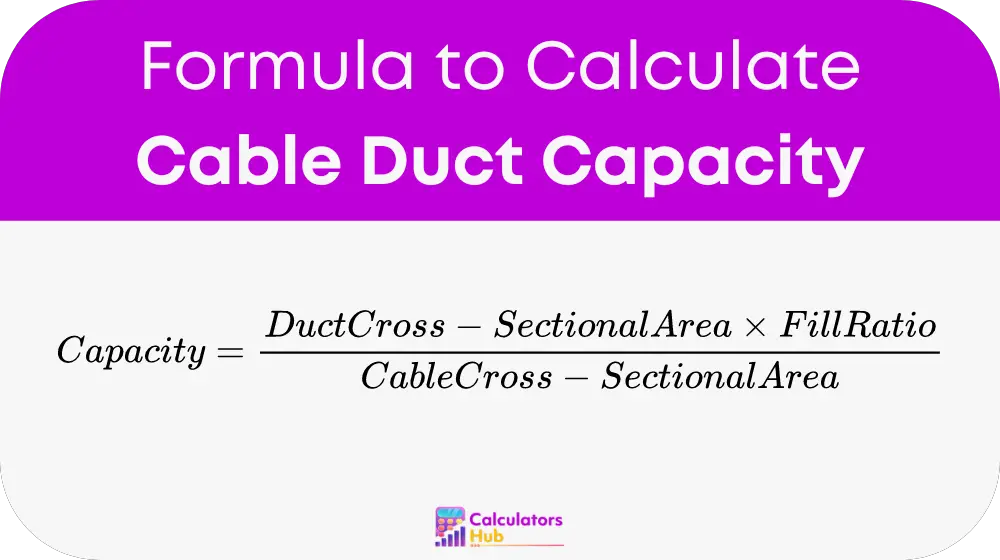
Where:
- Duct Cross-Sectional Area: The internal area of the cable duct, typically measured in square millimeters (mm²). This is the total space available inside the duct.
- Fill Ratio: The percentage of the duct that can be filled with cables. This is usually around 40%, as leaving space allows for airflow and prevents the cables from overheating or becoming difficult to access for future maintenance.
- Cable Cross-Sectional Area: The cross-sectional area of a single cable, also measured in square millimeters (mm²). This represents the amount of space each cable occupies within the duct.
By applying this formula, the calculator provides the maximum number of cables that can be safely housed within the duct.
Common Cable Duct Capacity Terms
Here’s a table outlining key terms related to cable ducts and their capacity, which will help users understand the calculations and make informed decisions when designing electrical systems.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Duct Cross-Sectional Area | The internal area of the cable duct, which determines how much space is available for cables. |
| Fill Ratio | The percentage of the duct that can be filled with cables, typically 40% to allow space for airflow. |
| Cable Cross-Sectional Area | The area occupied by one cable, measured in square millimeters (mm²), important for fitting cables within ducts. |
| Cable Trunking | Another term for cable ducting, used to organize and protect cables in installations. |
| Overfilling | A condition where too many cables are placed in the duct, potentially causing overheating or damage. |
| Ventilation | The airflow allowed within the duct, crucial for preventing cables from overheating. |
| Expansion Space | The extra space left in a duct to allow for future cable additions or maintenance access. |
| Conduit Fill | A term often used interchangeably with fill ratio, referring to the percentage of a duct or conduit filled by cables. |
| Insulated Cable | A cable that has a protective covering to prevent electrical shorts, usually increasing its cross-sectional area. |
Understanding these terms ensures that users can calculate the appropriate duct capacity and avoid common pitfalls like overfilling, which can lead to overheating or future access problems.
Example of Cable Duct Capacity Calculator
Let’s go through an example to demonstrate how the Cable Duct Capacity Calculator works.
Suppose you are installing cables in a duct with an internal cross-sectional area of 4000 mm². The recommended fill ratio is 40%, and each cable has a cross-sectional area of 100 mm².
Using the formula:
Cable Duct Capacity = (Duct Cross-Sectional Area * Fill Ratio) / Cable Cross-Sectional Area
Substitute the values:
Cable Duct Capacity = (4000 mm² * 0.4) / 100 mm²
Cable Duct Capacity = 1600 mm² / 100 mm² = 16 cables
In this case, you can safely fit 16 cables into the duct while maintaining a 40% fill ratio. This allows enough space for airflow and future adjustments or expansions.
Most Common FAQs
The fill ratio is crucial because it ensures that the duct is not overfill with cables, which can lead to overheating, reduced performance, or even electrical hazards. Typically, a fill ratio of 40% is recommend to allow for proper airflow and to leave space for future maintenance or expansions. Exceeding this ratio can make it difficult to add new cables or maintain the existing ones, while also increasing the risk of overheating due to restricted airflow.
To choose the correct duct size, you need to calculate the total cross-sectional area of all the cables you plan to install and apply the recommended fill ratio (usually 40%). This will give you the required duct cross-sectional area. Be sure to choose a duct that provides some extra space for future cable additions or changes in the system. Additionally, consider environmental factors like temperature and installation location, as these can affect the performance and durability of the cables.