The Bridge Rectifier Output Voltage Calculator helps users determine the direct current (DC) voltage output after the conversion of alternating current (AC) to DC using a bridge rectifier. A bridge rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a specific configuration to convert AC input into DC output, which is essential for many electronic devices and circuits.
The calculator simplifies the process by taking into account the input AC voltage, the RMS (root mean square) value, and the voltage drop across the diodes. Knowing the output voltage is critical for designing power supply systems, ensuring that the correct voltage is delivered to electronic components.
By using this calculator, engineers, technicians, and hobbyists can quickly calculate the expected DC output of a bridge rectifier, allowing them to plan and design circuits with the correct power specifications.
Formula
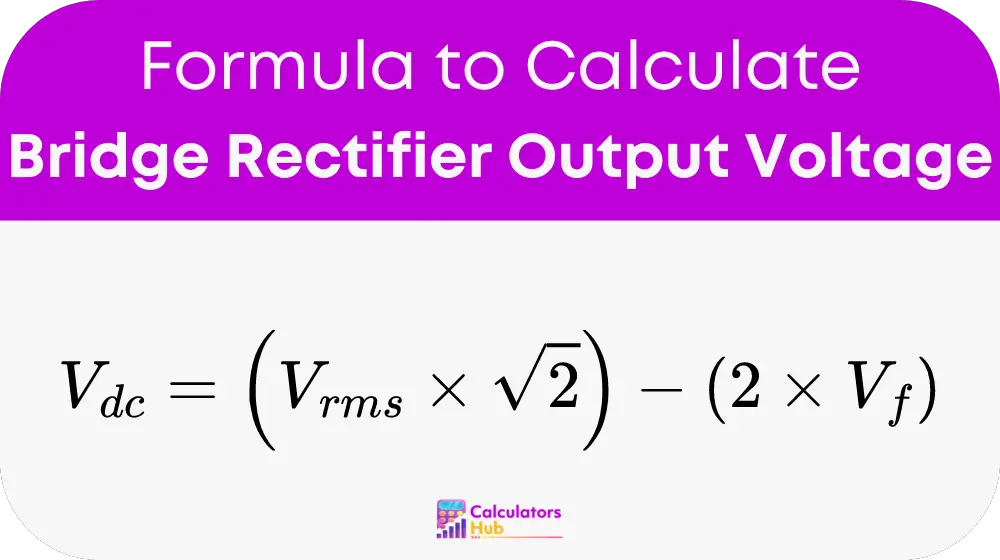
Variable Definitions:
- V_dc (Output DC Voltage): The rectified DC output voltage after the bridge rectifier (measured in volts).
- V_rms (AC Input RMS Voltage): The root mean square (RMS) value of the input AC voltage (measured in volts).
- V_f (Diode Forward Voltage Drop): The forward voltage drop across each diode in the rectifier. For typical silicon diodes, this value is usually around 0.7V per diode.
Formula Breakdown:
- V_dc (Output DC Voltage): This is the final DC voltage after the AC has been converted. It’s essential for ensuring that the output voltage matches the required specifications of the circuit.
- V_rms (AC Input RMS Voltage): The RMS value of the AC voltage is the effective value of the fluctuating AC voltage. This is commonly the value provided by AC power sources.
- V_f (Diode Forward Voltage Drop): The voltage drop that occurs across each diode when current flows through it. In a bridge rectifier, two diodes are in the current path at any time, which is why the voltage drop is doubled (2 × V_f).
General Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Bridge Rectifier | An arrangement of four diodes that converts AC to DC voltage. |
| DC Voltage (V_dc) | The output voltage after AC is converted into direct current. |
| AC Voltage (V_rms) | The input alternating current voltage, typically in the form of RMS value. |
| Diode Forward Voltage (V_f) | The voltage lost across a diode when current passes through it. |
| RMS (Root Mean Square) | A statistical measure used to define the effective voltage of an AC signal. |
| Full-Wave Rectification | The process of converting both halves of the AC waveform into DC. |
| Power Supply | A system that provides electrical power to a device, often converting AC to DC. |
| Voltage Regulation | The process of ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and consistent. |
| Silicon Diode | A type of diode commonly used in rectifiers, with a typical forward voltage drop of around 0.7V. |
Example
Let’s walk through an example to demonstrate how the Bridge Rectifier Output Voltage Calculator works.
Scenario:
You are designing a power supply system that uses an AC input voltage of 120V RMS and a bridge rectifier built with standard silicon diodes. Each diode has a forward voltage drop of 0.7V. You want to calculate the output DC voltage.
Step-by-step Calculation:
- AC Input RMS Voltage (V_rms):
V_rms = 120V - Diode Forward Voltage Drop (V_f):
V_f = 0.7V - Bridge Rectifier Output Voltage (V_dc):V_dc = (V_rms × √2) – (2 × V_f)
V_dc = (120 × 1.414) – (2 × 0.7)
V_dc = 169.68 – 1.4
V_dc ≈ 168.28V
Result:
The rectified DC output voltage is approximately 168.28V. This value can be used to power DC circuits that require stable and consistent voltage.
Most Common FAQs
The forward voltage drop represents the energy lost when current flows through a diode. In a bridge rectifier, two diodes are always in the current path, resulting in a total forward voltage drop of twice the value of a single diode. This reduces the overall output voltage, and it is important to account for this loss to ensure the correct voltage is deliver to your circuit.
RMS (root mean square) voltage is the effective value of an AC voltage, which represents the equivalent DC value in terms of energy delivery. Peak voltage, on the other hand, is the maximum instantaneous value of the voltage in an AC waveform. The RMS voltage is always lower than the peak voltage, and the relationship between them is given by the factor √2 (approximately 1.414).
When choosing diodes for a bridge rectifier, consider factors such as the forward voltage drop, maximum current rating, and reverse breakdown voltage. Silicon diodes with a forward voltage drop of around 0.7V are commonly use, but for higher efficiency, Schottky diodes with lower forward voltage drops may be prefer.