The Amps to Electrons Per Second Calculator translates electrical current measured in amperes into the equivalent number of electrons moving through a conductor each second. This calculation is essential for physicists, engineers, and technicians who work with electronic components and need to understand the detailed behavior of electrical currents at a microscopic level.
Variables:
- Current (I): The electric current in amperes (A).
- Elementary Charge (e): The charge of a single electron, approximately 1.602 × 10^-19 coulombs (C).
Formula of Amps To Electrons Per Second Calculator
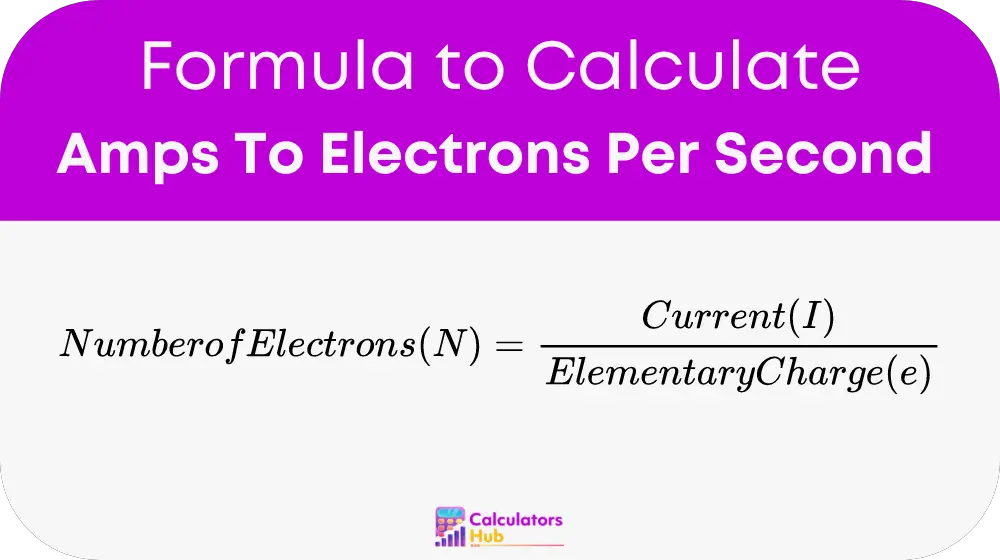
Detailed Calculation:
- Identify the Current (I): Measure or determine the electric current in amperes.
- Use the Elementary Charge (e): Recognize the charge of a single electron, approximately 1.602 × 10^-19 coulombs.
- Calculate the Number of Electrons per Second (N): Apply the formula to compute the number of electrons passing through the conductor per second.
Table of Common Calculations
For practical utility, a table of typical values calculated using the Amps to Electrons Per Second calculator is provided below. This reference helps users quickly determine the number of electrons per second for common current values without manual calculation.
| Current (A) | Electrons per Second |
|---|---|
| 0.001 | 6.242 × 10^15 |
| 0.01 | 6.242 × 10^16 |
| 0.1 | 6.242 × 10^17 |
| 1 | 6.242 × 10^18 |
| 10 | 6.242 × 10^19 |
Example of Amps To Electrons Per Second Calculator
Imagine a device that draws 0.005 amperes of current. To find out how many electrons pass through it per second, use the calculator:
- Current (I): 0.005 A
- Calculation: Number of Electrons per Second (N) = 0.005 A / 1.602 × 10^-19 C ≈ 3.121 × 10^16 electrons per second
This result shows that approximately 31.21 quadrillion electrons flow through the conductor each second at this current level.
Most Common FAQs
Understanding electron flow at this level is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electronic circuits, as well as for educational purposes in physics and engineering.
This calculator is primarily designed for direct current (DC) applications, as AC calculations require considerations of peak and average values due to the changing nature of the current.
The accuracy depends on the precision of the input values. However, the fundamental constants used, like the elementary charge, are defined with high precision, ensuring reliable calculations.