An Amps Per Phase Calculator is essential for understanding the current load in each phase of a multi-phase electrical system, crucial for system stability and efficiency, especially in industrial settings.
Formula of Amps Per Phase Calculator
To calculate the current per phase, the formula used is:
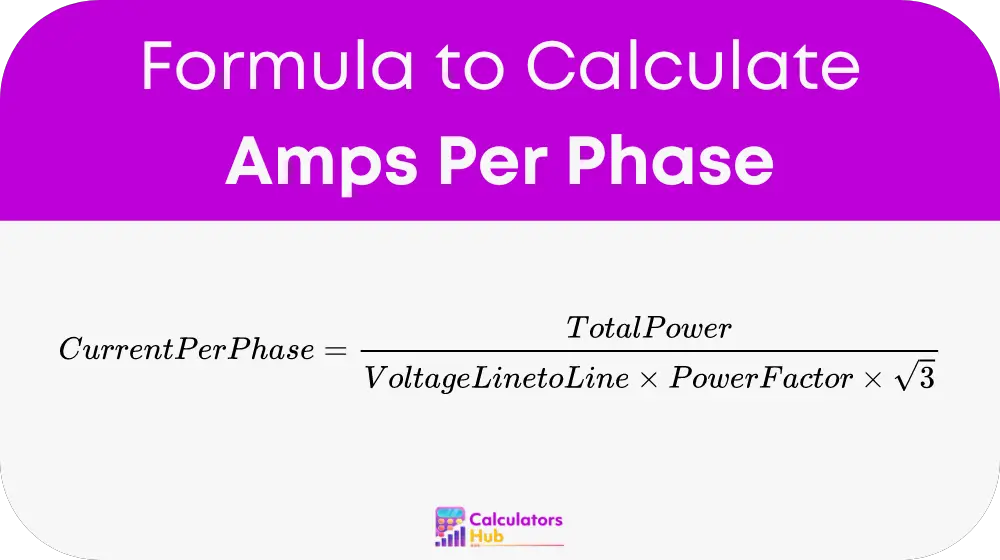
Variables and Calculation:
- Total Power (P): The total power consumption in watts.
- Voltage Line-to-Line (V_L-L): The voltage between two phases in volts.
- Power Factor (PF): A ratio indicating the efficiency of the power usage, typically a number between 0 and 1.
- Calculate the Current Per Phase (I): Using the above variables, apply the formula to determine the current in each phase.
Reference Table for General Electrical Terms
Here is a table with general terms and their meanings to help users understand the basics without needing calculations for everyday applications:
| Term | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Watts (Power) | Measure of electrical power | 1000 watts |
| Volts (Voltage) | Measure of electrical potential | 120 volts |
| Amperes (Current) | Measure of electrical current | 10 amperes |
Example of Amps Per Phase Calculator
For a system using 1500 watts at 120 volts with a power factor of 0.95:
Current Per Phase = 1500 / (120 × 0.95 × sqrt(3)) ≈ 7.23 amps
This example demonstrates how to calculate the current for one phase in a typical three-phase system.
Most Common FAQs
The power factor can usually be obtained from system specifications or measured using specialized equipment.
The formula can be adjusted by changing the square root component according to the number of phases, but the typical calculation assumes three phases.
Yes, it’s adaptable to various settings as long as the correct inputs are provided.