The Ampere's Law Calculator is an invaluable tool for physicists, engineers, and students involved in electromagnetic studies. It leverages Ampere's Law to determine the magnetic field created by an electric current flowing through a conductor. This law is a fundamental principle of electromagnetism that relates the integrated magnetic field around a closed loop to the electric current passing through that loop.
Formula of Ampere’s Law Calculator
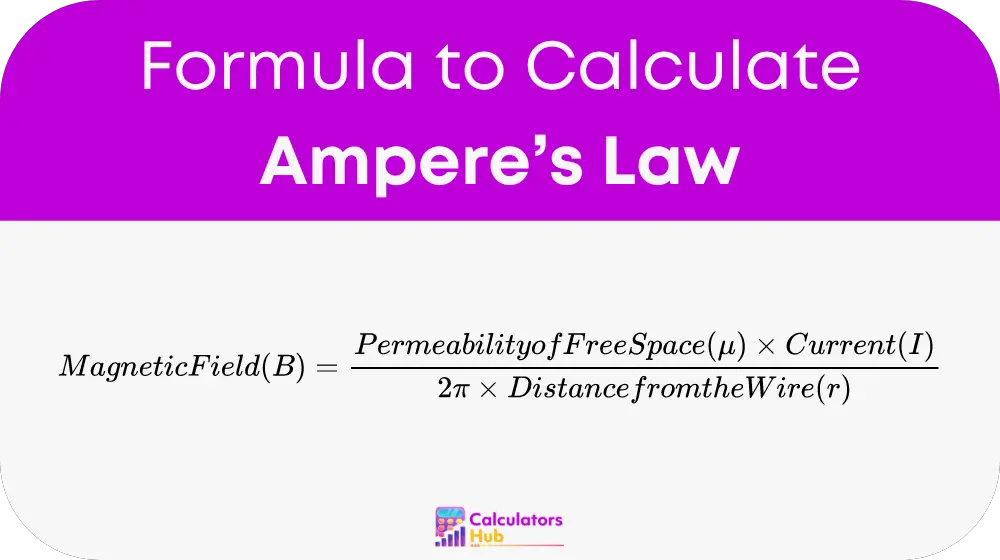
Ampere's Law provides a method to calculate the magnetic field based on the current and the geometry of the conductor:
Variables:
- Magnetic Field (B): The magnetic field around the conductor, measured in teslas (T).
- Permeability of Free Space (μ₀): A physical constant approximately equal to 4π × 10^-7 T·m/A, which relates magnetic field and magnetic flux density.
- Current (I): The electric current flowing through the conductor, measured in amperes (A).
- Distance from the Wire (r): The perpendicular distance from the conductor to the point where the magnetic field is calculated, measured in meters (m).
Formula:
Detailed Calculation:
- Identify the Current (I): Measure or estimate the current passing through the conductor.
- Determine the Distance from the Wire (r): Measure the perpendicular distance from the wire to the point at which the magnetic field is to be calculated.
- Use the Permeability of Free Space (μ₀): Apply the constant value, 4π × 10^-7 T·m/A, to account for the inherent properties of the space around the conductor.
- Calculate the Magnetic Field (B): Employ the formula to ascertain the strength of the magnetic field at the specified distance from the conductor.
Table for General Terms
This table defines key terms used in conjunction with the Ampere’s Law Calculator:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Magnetic Field (B) | The magnetic influence produced by electric currents and magnetic materials. |
| Permeability of Free Space (μ₀) | A constant that provides a measure of the ability of the vacuum to support magnetic fields. |
| Ampere (A) | The unit of electric current in the International System of Units. |
| Tesla (T) | The unit of magnetic flux density or magnetic inductivity. |
Example of Ampere’s Law Calculator
For instance, if a conductor carries a current of 5 amperes and the point of interest is 0.1 meters from the conductor:
- Current (I) = 5 A
- Distance from the Wire (r) = 0.1 m
Magnetic Field (B) = (4π × 10^-7 T·m/A × 5 A) / (2π × 0.1 m) = 1 × 10^-5 T
This result shows that the magnetic field at 0.1 meters from the conductor is 10 microteslas.
Most Common FAQs
A1: The calculator is highly accurate provided the input values are correct. It is based on fundamental physical constants and laws of electromagnetism.
A2: Ampere's Law is generally apply to long, straight conductors, solenoids, and toroids, where symmetry simplifies calculations. For more complex configurations, numerical methods or integral calculus may be require.
A3: The permeability of free space is crucial as it dictates how magnetic fields interact with physical space and is essential for calculating magnetic fields in vacuum conditions.