The Active Power Calculator helps users determine the real power consumed by an electrical system when voltage, current, and phase difference are known. This tool is essential for optimizing electrical load and efficiency in various applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery.
Formula of Active Power Calculator
To calculate active power (P) in watts (W), the formula is:
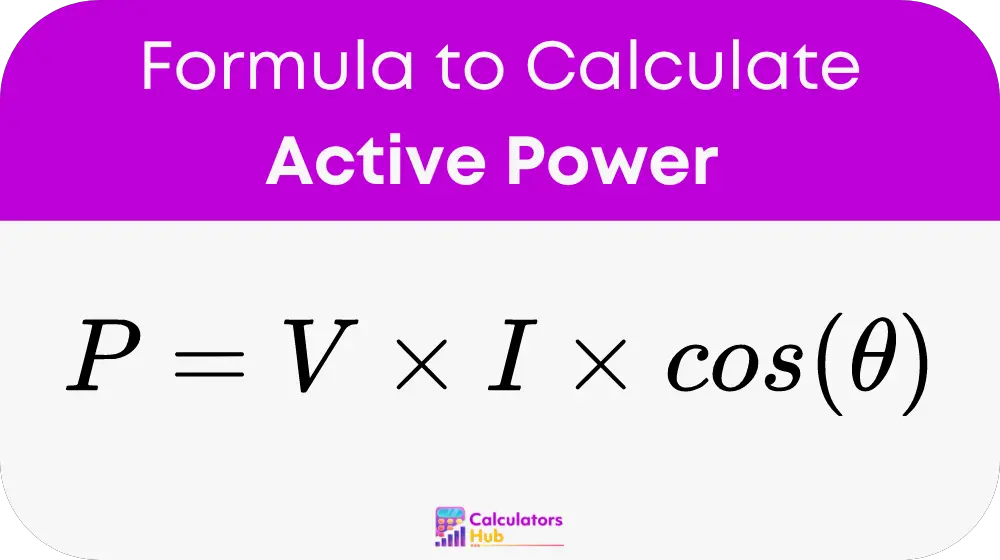
- V is the voltage in volts (V).
- I is the current in amperes (A).
- cos(theta) is the power factor, representing the cosine of the phase angle between the voltage and current.
For accurate measurements:
- Voltage (V): Measure the RMS value of the voltage.
- Current (I): Measure the RMS value of the current.
- Power Factor (cos(theta)): Determine by the ratio of true power to apparent power:
- cos(theta) = True Power / Apparent Power
- True Power is the actual power in watts, while Apparent Power is the product of RMS voltage and current in volt-amperes (VA).
Table for General Terms and Calculations
This table includes common electrical terms related to the calculation of active power, along with their definitions and some typical conversions that can help in quick calculations without the need for detailed computations.
| Term | Definition | Example Values/Conversions |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | The electrical potential difference | 230 V (household supply), 400 V (industrial supply) |
| Current (I) | The flow of electric charge | 10 A (small devices), up to 100 A (large machinery) |
| Power Factor | The ratio of real power flowing to the load to the apparent power in the circuit | 0.8 (typical for motors), 1.0 (ideal condition) |
| Active Power (P) | The actual power in watts consumed by the device | Calculated as P = V * I * cos(θ) |
| Phase Angle (θ) | The angle of phase difference between voltage and current | 30° (common in AC systems), varies with load |
| True Power | Real power consumed by the load, in watts | Depends on system efficiency and load |
| Apparent Power | Total power in volt-amperes, includes active and reactive power | V * I (without considering phase angle) |
| RMS (Root Mean Square) | Measurement of the magnitude of a varying quantity | Typically used for V and I in AC circuits |
Example of Active Power Calculator
Imagine needing to calculate the active power for a motor running at 230 volts with a current of 5 amperes and a power factor of 0.85. The process would be as follows:
- Insert the values into the formula:
- P = 230 * 5 * 0.85
- Calculate the result:
- P = 977.5 watts
This example demonstrates the calculator’s utility in practical settings, ensuring efficient energy use and system design.
Most Common FAQs
Active power is the actual power consumed by devices in performing work, while reactive power is the power stored temporarily in the system, necessary for maintaining the voltage levels across the grid.
Yes, the Active Power Calculator is versatile and can be used across various alternating current (AC) systems, provided the correct inputs are given.