A Deck Angle Calculator helps engineers, architects, shipbuilders, and aviation professionals determine the inclination of a deck relative to a horizontal reference point. This calculation is essential for maritime stability analysis, aircraft takeoff and landing angles, and structural design in construction.
The deck angle provides insight into how much a surface is tilted from a level position, which is crucial in ship navigation, aircraft performance assessments, and safe deck construction. By calculating the deck angle, professionals can ensure that a structure or platform is within a safe and functional range of inclination.
Formula for Deck Angle Calculator
The Deck Angle (θ) is determined using the inverse tangent (arctan) function as follows:
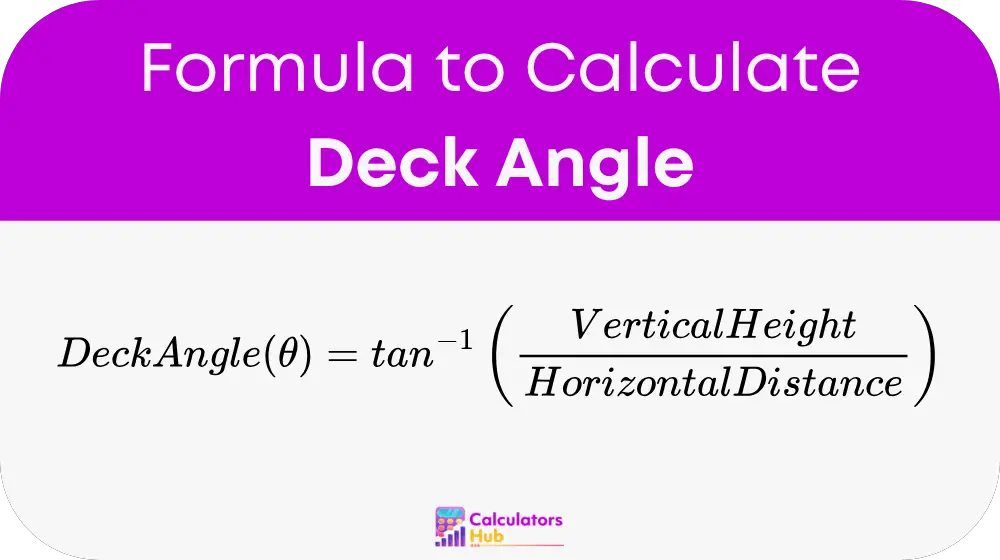
Where:
θ = Deck angle (in degrees)
Vertical Height = Height of the deck above the reference point (m or ft)
Horizontal Distance = Distance from the base to the reference point (m or ft)
tan⁻¹ = Inverse tangent function (arctan)
This formula calculates the angle of inclination by comparing the rise (vertical height) to the run (horizontal distance). The greater the vertical height relative to the horizontal distance, the steeper the deck angle.
Deck Angle Reference Table
The following table provides estimated deck angles for various height-to-distance ratios, offering a quick reference for professionals working with inclined surfaces.
| Vertical Height (m) | Horizontal Distance (m) | Deck Angle (θ) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 5.71° | Mild slope (walkways, gentle inclines) |
| 2 | 10 | 11.31° | Standard ship deck tilt in calm waters |
| 3 | 10 | 16.70° | Moderate aircraft climb angle |
| 4 | 10 | 21.80° | Steep ship inclination in rough waters |
| 5 | 10 | 26.57° | Critical tilt for heavy construction platforms |
| 10 | 10 | 45.00° | Extreme incline, typically avoided |
This table helps ship designers, pilots, and construction engineers estimate safe deck inclinations without requiring manual calculations.
Example of Deck Angle Calculator
A ship's deck is tilted due to rough sea conditions. The vertical rise is 2.5 meters, and the horizontal base distance is 12 meters.
Step 1: Apply the Deck Angle Formula
θ = tan⁻¹ (2.5 / 12)
Step 2: Compute the Ratio
θ = tan⁻¹ (0.2083)
Step 3: Compute the Angle
θ ≈ 11.79°
This means the ship's deck is tilte at an angle of approximately 11.79°, which is within a safe range for normal operations.
Most Common FAQs
The deck angle affects passenger safety, cargo stability, and navigational efficiency. A high deck angle in rough waters can lead to difficulty in movement, structural stress, and tipping hazards.
Aircraft need an optimal deck angle (climb angle) to achieve efficient lift while maintaining safe aerodynamic performance. A steep angle can cause excessive drag, while a low angle may not generate enough lift.
Yes, deck angle calculations help engineers design safe ramps, bridges, and building platforms, ensuring that structural inclines comply with safety regulations and are comfortable for human use.