The PSU Calculator estimates the total power consumption of all the components in your computer system, ensuring you select a PSU that can handle the load. By accurately calculating the wattage requirements, it prevents issues such as power shortages, component damage, and system instability. The calculator considers each component’s power draw and sums them up to provide a recommended PSU wattage.
Formula of PSU Calculator
The formula for calculating the total wattage requirement for a computer is straightforward:
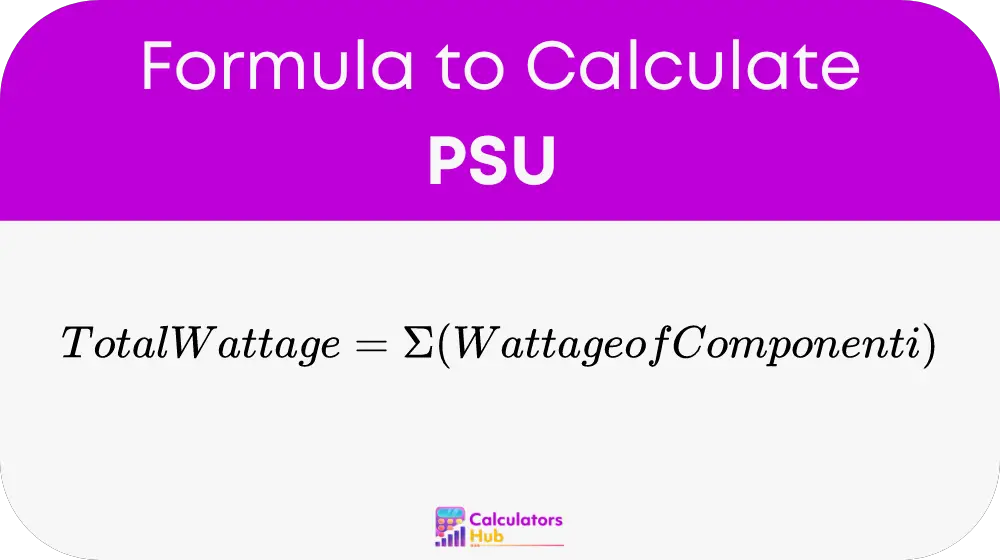
Where:
- Wattage of Component i: The power consumption of each individual component in the computer.
Here are the typical wattages for common components:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit):
- Typical range: 65W – 150W (depending on the model and usage)
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit):
- Typical range: 150W – 350W (depending on the model and usage)
- Motherboard:
- Typical range: 50W – 100W (depending on the model and features)
- RAM (Random Access Memory):
- Typical range: 2W – 5W per stick
- Storage (HDD/SSD):
- HDD: 6W – 9W per drive
- SSD: 2W – 4W per drive
- Optical Drive:
- Typical range: 15W – 25W
- Fans:
- Typical range: 2W – 5W per fan
- Peripherals:
- Typical range: varies, but usually around 5W – 10W per device
Table of General Terms
Here’s a table of general terms associated with PSU calculators:
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| PSU (Power Supply Unit) | A hardware component that provides power to a computer system. |
| Wattage | A measure of electrical power expressed in watts (W). |
| Component | Individual parts of a computer, such as the CPU, GPU, and RAM. |
| Power Consumption | The amount of power a component uses, measured in watts (W). |
Example of PSU Calculator
Consider a computer with the following components:
- CPU: 95W
- GPU: 250W
- Motherboard: 70W
- RAM: 4 sticks at 4W each (16W total)
- Storage: 1 HDD at 8W and 1 SSD at 3W (11W total)
- Optical Drive: 20W
- Fans: 3 fans at 4W each (12W total)
- Peripherals: 3 devices at 6W each (18W total)
Total Wattage Calculation:
- CPU: 95W
- GPU: 250W
- Motherboard: 70W
- RAM: 16W
- Storage: 11W
- Optical Drive: 20W
- Fans: 12W
- Peripherals: 18W
Total Wattage = 95 + 250 + 70 + 16 + 11 + 20 + 12 + 18 = 492W
In this example, a PSU with a wattage of at least 550W is recommended to ensure stability and allow for some headroom.
Most Common FAQs
It is generally recommended to have at least a 20% overhead above your calculated total wattage to ensure reliability and future-proofing for potential upgrades.
Yes, using a PSU with a higher wattage than needed is perfectly safe and can be beneficial for system stability and longevity.
It’s advisable to review your PSU requirements whenever you upgrade major components such as the CPU or GPU to ensure your PSU can handle the new power demands.