The Bits Per Sample (BPS) Calculator is a tool used to determine the number of bits needed to represent each sample in a digital signal processing system. This value is essential for understanding the precision and quality of the signal. A higher Bits Per Sample value indicates greater accuracy in representing the signal amplitude, while a lower value suggests reduced precision. By calculating BPS, users can evaluate and optimize the quality of digital audio or other sampled data.
Formula of Bits Per Sample Calculator
To calculate Bits Per Sample, use the following formula:
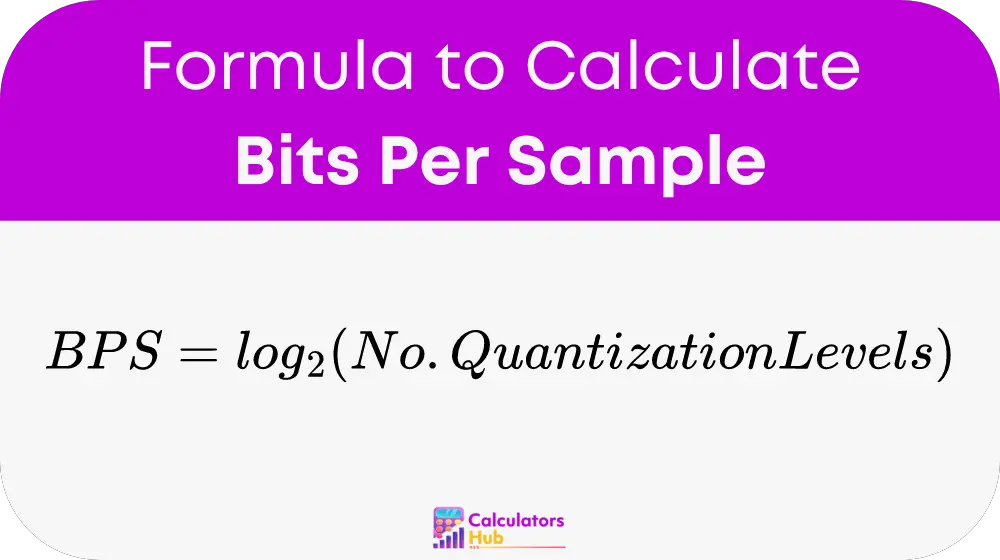
Where:
- Number of Quantization Levels: The total number of distinct levels used to represent the amplitude of the signal in each sample.
Steps to Calculate Bits Per Sample
- Determine the Number of Quantization Levels: Identify the total number of levels used to represent the amplitude of the signal. This is usually defined by the resolution of the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or digital signal processor (DSP).
- Calculate the Bits Per Sample: Use the logarithm base 2 (log₂) of the number of quantization levels to find the bits per sample. This calculation reveals how many bits are used to encode each sample.
General Reference Table
This table provides common values for Bits Per Sample and the corresponding number of quantization levels. It can help users quickly understand the relationship between BPS and quantization levels without additional calculations.
| Bits Per Sample | Number of Quantization Levels |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 8 | 256 |
| 16 | 65,536 |
Example of Bits Per Sample Calculator
Let’s calculate the Bits Per Sample for a system with 256 quantization levels.
- Determine the Number of Quantization Levels: The system uses 256 levels.
- Apply the Formula:Bits Per Sample = log₂(256)To find the BPS, calculate the logarithm base 2 of 256.Bits Per Sample = log₂(256) = 8This result means that the system uses 8 bits to represent each sample.
Most Common FAQs
BPS is important because it determines the precision with which an analog signal is convert to digital form. Higher BPS values mean that the signal can be represent more accurately, which is crucial for high-quality audio and precise measurements in digital systems. Understanding BPS helps in selecting appropriate hardware and optimizing data quality.
In digital audio, higher BPS values result in better sound quality because they allow for more precise representation of the audio signal's amplitude. For example, 16-bit audio provides more detail and dynamic range than 8-bit audio. Therefore, higher BPS values reduce quantization noise and improve overall audio fidelity.
Yes, the Bits Per Sample Calculator is applicable to various types of sampled signals, not just audio. It can be use to evaluate the precision of any digital system that involves analog-to-digital conversion, such as image processing and sensor data acquisition.