The Number of Nuclei Calculator calculates the remaining number of nuclei in a sample after a certain period. This calculation is crucial in fields like nuclear physics, medicine, and environmental science, where understanding the behavior of radioactive materials is essential. By using this calculator, you can predict how a sample will change over time, which is critical for safety, research, and practical applications.
Formula of Number of Nuclei Calculator
The number of remaining nuclei N(t) after time t can be calculated with:
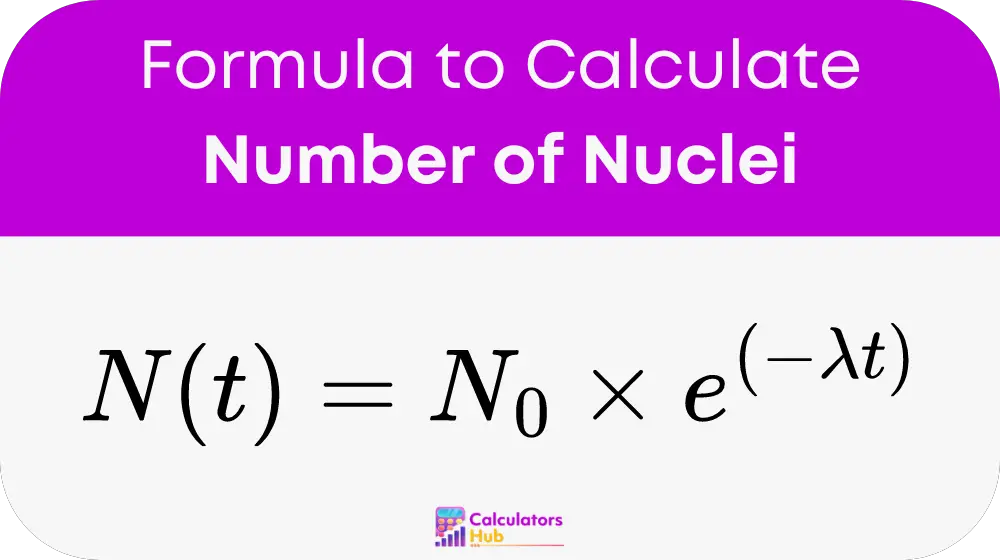
Where:
- N(t) is the number of nuclei remaining after time t
- N0 is the initial number of nuclei
- λ is the decay constant
- t is the elapsed time
- e is the base of the natural logarithm
General Terms Table
To make it easier, here are some pre-calculated values based on common parameters:
| Initial Nuclei (N0) | Decay Constant (λ) | Time (t) | Remaining Nuclei (N(t)) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 | 0.01 | 100 | 368.0 |
| 1000 | 0.02 | 50 | 367.9 |
| 500 | 0.01 | 200 | 135.3 |
| 500 | 0.02 | 100 | 135.3 |
| 100 | 0.05 | 20 | 36.8 |
Example of Number of Nuclei Calculator
Let’s consider an example to understand how the Number of Nuclei Calculator works. Suppose we have an initial number of nuclei N0 = 1000, a decay constant λ = 0.01, and an elapsed time t = 100.
Using the formula:
N(100) = 1000 * e^(-0.01 * 100)
N(100) ≈ 1000 * 0.3679 ≈ 367.9
Therefore, after 100 units of time, approximately 367.9 nuclei remain.
Most Common FAQs
The decay constant (λ) is a probability rate at which a given nucleus will decay per unit time. It is specific to each radioactive isotope and is a crucial part of the decay process.
The accuracy of the Number of Nuclei Calculator depends on the precision of the input values. The calculator itself uses a well-established formula that is accurate for modeling radioactive decay.
Yes, this calculator can be used for any type of radioactive nuclei as long as the decay constant (λ) is known. It applies universally to all types of nuclear decay processes.