The Effective Diffusivity Calculator estimates the rate at which a substance diffuses through a porous material, considering how porosity and tortuosity affect the movement of particles. It is a crucial tool in chemical engineering, environmental science, and material science.
In porous systems like soils, catalysts, or membranes, particles do not travel in a straight line. Instead, they follow a complex path due to pores and barriers. The calculator helps researchers and engineers adjust bulk diffusion values to reflect real-world transport conditions.
This tool is part of the Chemical Engineering and Material Science Calculators category.
formula of Effective Diffusivity Calculator
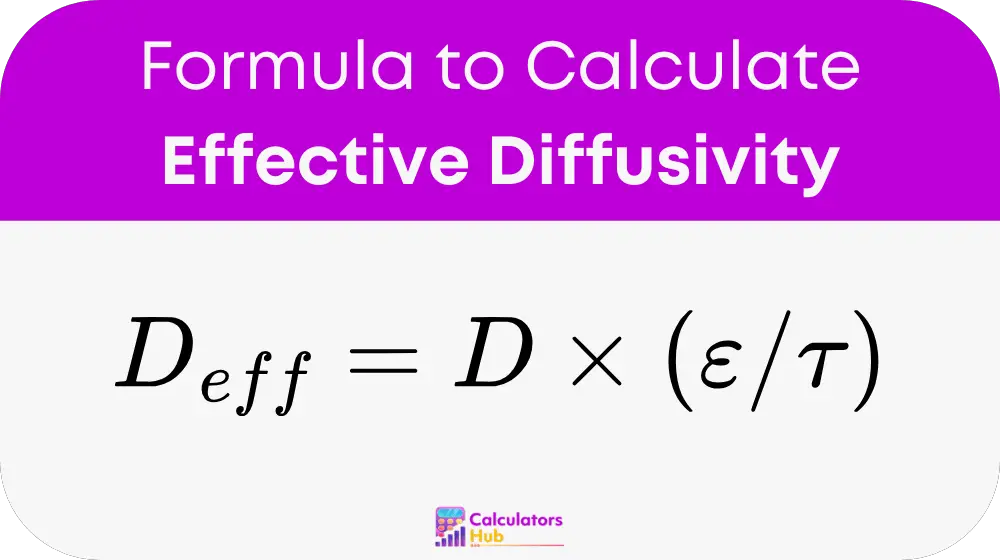
Explanation of Variables:
D_eff:
Effective Diffusivity — this is the adjusted diffusion coefficient that reflects how substances move through a porous medium. Units are typically in m²/s or cm²/s.
D:
Bulk Diffusivity — this is the diffusion rate in an open, non-restrictive medium like air or water. Use the same units as for D_eff.
ε (epsilon):
Porosity — the fraction of the total volume of the material that is made up of voids or pores. It is dimensionless and ranges between 0 (no pores) and 1 (completely porous).
τ (tau):
Tortuosity — the measure of how winding or twisted the path is for the diffusing particles. It is dimensionless, and usually greater than 1. The higher the tortuosity, the more difficult it is for particles to move through the medium.
This formula helps simulate how efficiently substances like gases, liquids, or ions travel through porous barriers under real conditions.
Reference Table for Quick Values and Practical Conversion Info
| Material Type | Porosity (ε) | Tortuosity (τ) | Typical D_eff / D Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packed Sand | 0.35 | 2.5 | 0.14 |
| Clay Soil | 0.45 | 4.0 | 0.11 |
| Open Foam | 0.80 | 1.5 | 0.53 |
| Activated Carbon | 0.60 | 3.0 | 0.20 |
| Ceramic Filter | 0.25 | 2.0 | 0.13 |
Quick Conversion:
- To convert from cm²/s to m²/s, divide by 10,000
- To convert from m²/s to cm²/s, multiply by 10,000
This table is helpful for engineers and researchers who want approximate estimates without doing full calculations.
Example of Effective Diffusivity Calculator
Problem:
Calculate the effective diffusivity of a gas diffusing through activated carbon.
Given:
- Bulk Diffusivity, D = 1.2 × 10⁻⁵ m²/s
- Porosity, ε = 0.60
- Tortuosity, τ = 3.0
Step 1: Apply the formula
D_eff = 1.2 × 10⁻⁵ × (0.60 / 3.0)
D_eff = 1.2 × 10⁻⁵ × 0.20 = 2.4 × 10⁻⁶ m²/s
Result:
The effective diffusivity in the activated carbon is 2.4 × 10⁻⁶ m²/s
Most Common FAQs
A: In porous materials, particles take longer paths and encounter resistance. Porosity reduces space, and tortuosity makes the path longer. Together, they reduce the actual diffusion rate compared to free space.
A: Yes. This model works for both gases and liquids diffusing through porous media, provided you know the bulk diffusivity and material characteristics.
A: Yes. A tortuosity of 1 means a straight path, which rarely happens in porous systems. In real cases, it’s typically between 1.5 and 5 or more.