This calculator utilizes the principles of spectrophotometry, a technique that measures how much a chemical substance absorbs light by measuring the intensity of light as a beam passes through sample solution. The key metric here is absorbance, which is directly proportional to the concentration of the solution under investigation. This relationship forms the basis for the calculator's function.
Formula of Concentration From Absorbance and Wavelength Calculator
The formula for calculating concentration from absorbance and wavelength is derived from the Beer-Lambert Law:
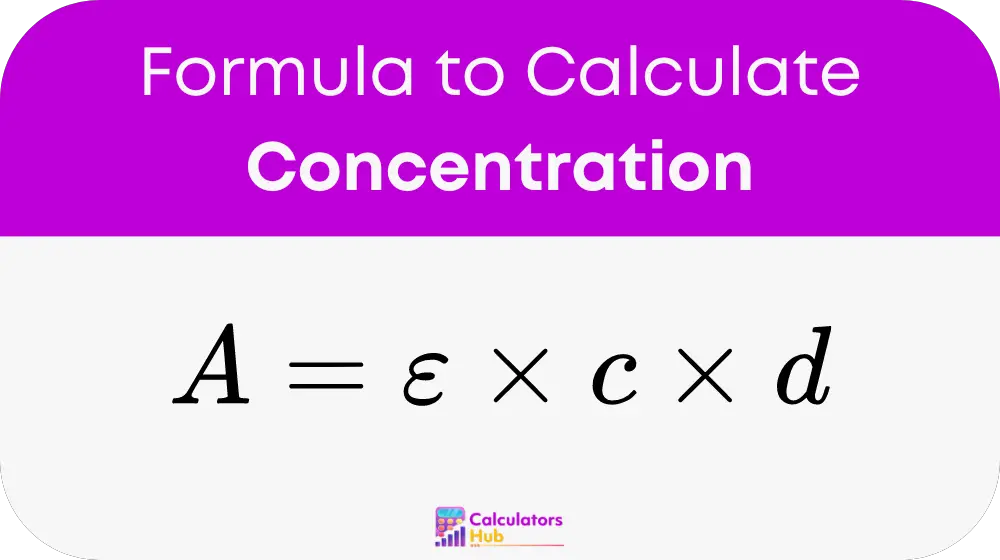
Where:
- A is the absorbance,
- epsilon is the molar absorptivity,
- c is the concentration,
- d is the path length of the cuvette.
To find the concentration, we rearrange the formula as follows:
c = A / (epsilon * d)
This simple yet powerful formula allows for quick calculations of concentration when the other variables are known.
Table of General Terms and Relevant Calculators
| Term | Definition | Related Calculator |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance (A) | Measure of the amount of light absorbed by a solution | Absorbance Calculator |
| Molar Absorptivity (epsilon) | Constant that quantifies how strongly a substance absorbs light at a given wavelength | Molar Absorptivity Finder |
| Path Length (d) | The distance that light travels through the sample | Path Length Calculator |
Example of Concentration From Absorbance and Wavelength Calculator
Let's consider a sample with an absorbance of 0.5, using a substance with a molar absorptivity of 100 L/mol*cm, and a path length of 1 cm:
c = 0.5 / (100 * 1) = 0.005 mol/L
This example demonstrates how the calculator can be used to quickly determine the concentration of a solution.
Most Common FAQs
A1: The accuracy depends on the precision of the input values. With precise measurements, the calculator provides highly accurate results.
A2: Yes, as long as you know the molar absorptivity of the substance at the specific wavelength and the path length of the cuvette.