Bomb calorimetry involves burning a sample to determine its energy content. The Bomb Calorimetry Calculator helps automate the calculations required to determine the heat of combustion of a substance. This tool is invaluable for chemists, students, and professionals who require quick and accurate energy measurements without manual computations.
Formula of Bomb Calorimetry Calculator
At the heart of bomb calorimetry calculations is the formula:
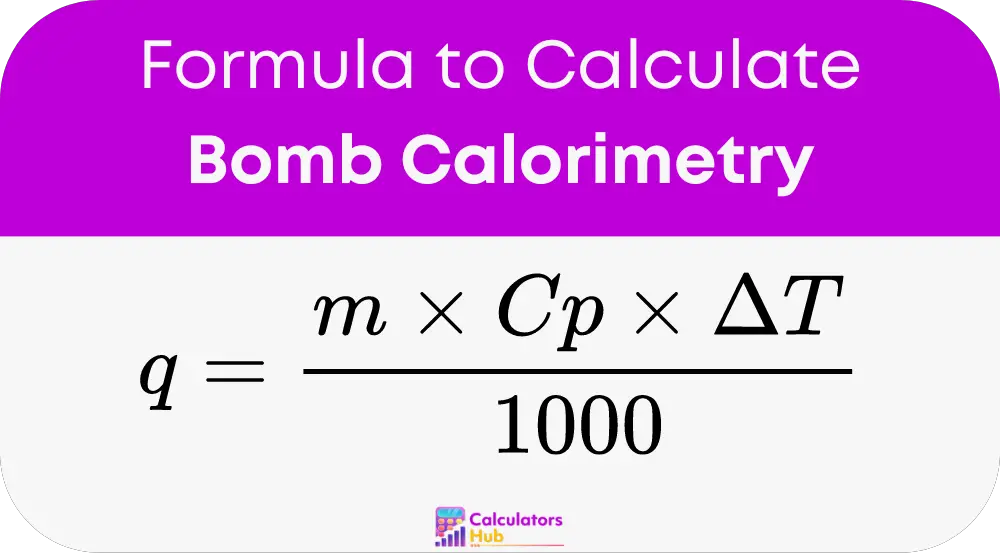
- q: The heat released or absorbed by the substance, measured in joules.
- m: The mass of the substance in grams.
- Cp: The specific heat capacity, which is the amount of heat per gram per degree Celsius.
- ΔT: The change in temperature of the substance in degrees Celsius.
Understanding this formula is crucial for effectively using the bomb calorimetry calculator.
Table for General Terms
Here’s a handy table of general terms and some typical specific heat capacities:
| Term | Definition | Example Values |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Heat Capacity (Cp) | Heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1°C. | Water: 4.18 J/g°C |
| Heat Capacity | Total heat capacity of the calorimeter system. | Varies by system design |
This table serves as a quick reference to aid in your calculations.
Example of Bomb Calorimetry Calculator
Let’s calculate the energy content of a 10g sample of substance with a specific heat capacity of 2.0 J/g°C and a temperature increase of 5°C:
q = (10 * 2.0 * 5) / 1000 = 0.1 joules
This example demonstrates the straightforward application of the formula using the calculator.
Most Common FAQs
The calculator is highly accurate provided that the input values are correct and precise.
Yes, but the user must ensure correct values for specific heat capacity and mass are entered.
It cannot measure the calorific value of substances that do not combust completely or that react with the bomb material.