In the realm of chemistry, the Apparent Molar Volume Calculator emerges as a crucial tool for analyzing solutions at a molecular level. It provides an accurate measure of the volume one mole of a solute occupies within a solution, adjusted for the volume of the solvent. This measurement is essential for chemists and researchers focusing on solution properties and interactions between solutes and solvents. Understanding these interactions is key in fields such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental technology, where solution behavior significantly influences product efficiency and sustainability.
Formula for Apparent Molar Volume Calculator
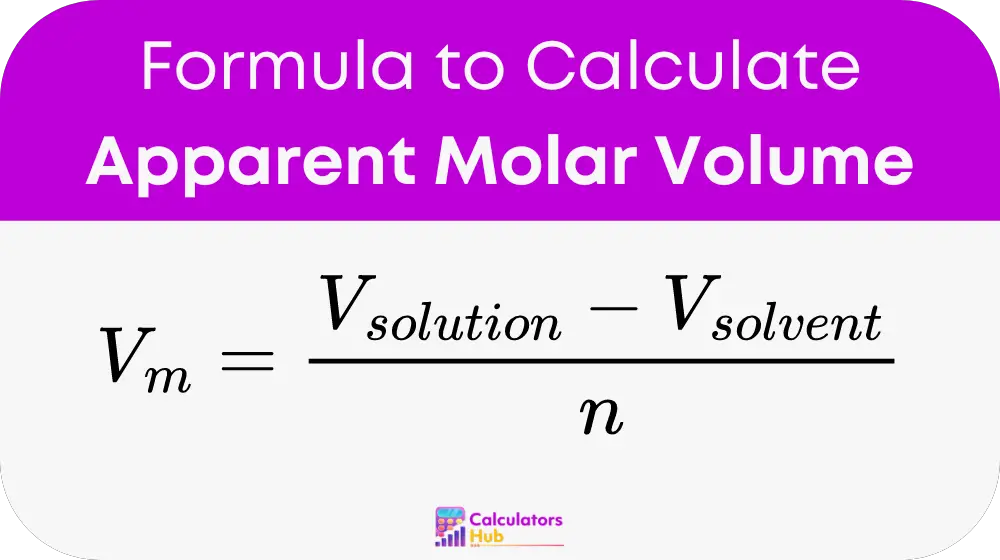
The calculation of apparent molar volume (V_m) is crucial for determining how solutes interact within their solvent environments, affecting solution characteristics like density and viscosity. The formula used is:
Detailed Breakdown:
- V_m: Apparent molar volume, typically in liters per mole.
- V_solution: Total volume of the solution.
- V_solvent: Volume of the solvent before adding the solute.
- n: Amount of solute in moles added to the solvent.
This formula helps in determining how much space each mole of solute occupies in the solution, which is vital for understanding solute-solvent interactions and their implications on the solution’s physical properties.
Practical Application: Reference Table
To aid practical application and enhance understanding, here is a reference table that provides an overview of typical apparent molar volumes for common solutes in water at room temperature:
| Solute | Apparent Molar Volume (cm³/mol) |
|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride | 16.2 |
| Glucose | 75.4 |
| Ethanol | 58.0 |
| Urea | 40.0 |
These values can vary based on temperature, pressure, and concentration, highlighting the need for precise calculations.
Example of Apparent Molar Volume Calculator
Consider a scenario where you dissolve 0.1 moles of sodium chloride in enough water to make 1 liter of solution. If the volume of the pure water was initially 0.995 liters, the calculation would be as follows:
- V_solution: 1 liter
- V_solvent: 0.995 liters
- n (moles of NaCl): 0.1 mol
Using the formula:
- Apparent Molar Volume (V_m) = (1 – 0.995) / 0.1 = 0.05 liters/mol
This example demonstrates how the calculator can be utilized to measure the change in volume attributable to the dissolved solute.
Most Common FAQs
In industries like pharmaceuticals and materials science, knowing the apparent molar volume helps in designing solutions with desired properties, such as optimal solubility and stability.
Temperature can significantly impact the volume of both the solvent and the solution, hence affecting the apparent molar volume. Increased temperatures typically increase the volume due to thermal expansion.
Yes, changes in apparent molar volume can indicate interactions between solute particles and the solvent, providing insights into molecular arrangement and interaction strength.