This calculator provides a user-friendly interface to compute the acid ionization constant for a variety of acids. By inputting the concentrations of hydrogen ions, the conjugate base, and the undissociated acid, users can quickly determine the Ka value, which is essential for predicting the behavior of acids in different chemical reactions.
Acid Ionization Constant Formula
The formula used by the calculator is:
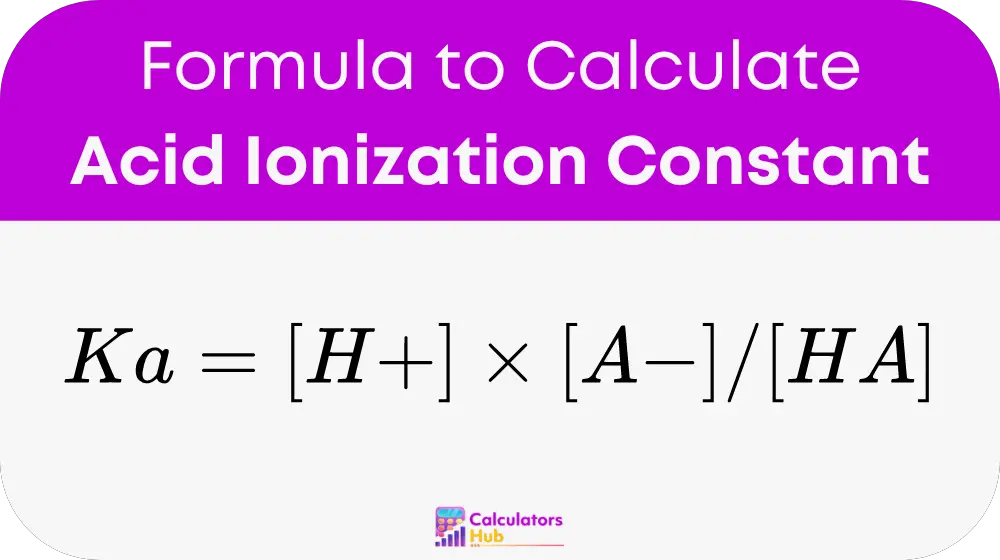
Where:
- [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in moles per liter (M).
- [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base in moles per liter (M).
- [HA] is the concentration of the undissociated acid in moles per liter (M).
Steps for Calculation:
- Measure or calculate [H+]: This can typically be done using a pH meter or from known pH values.
- Determine [A-]: Measure or calculate the concentration of the conjugate base.
- Ascertain [HA]: Determine the concentration of the undissociated acid.
- Substitute into formula: Use the measured values to calculate Ka.
Conversion Table for Acid Ionization Constants
| Acid | Ka Value | pH Range |
|---|---|---|
| Acetic Acid | 1.75 x 10^-5 | 2.4 – 3.4 |
| Hydrochloric Acid | High (strong acid) | < 1 |
| Citric Acid | 8.4 x 10^-4 | 3.1 – 4.5 |
Example of Acid Ionization Constant Calculator
Calculating the Ka for Acetic Acid:
- [H+]: 0.0001 M (from pH 4)
- [A-]: 0.0001 M (assuming equal dissociation)
- [HA]: 0.1 M (initial concentration minus dissociated amount)
- Ka Calculation: Ka = (0.0001 * 0.0001) / 0.1 = 1.75 x 10^-5
Most Common FAQs
A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, which dissociates more in solution.
This calculator is specifically designed for acids; however, the principle can be adapted for bases using Kb values.
Yes, but separate calculations are needed for each dissociation step.