In various fields, especially project management and human resources, accurately determining the amount of work completed relative to time is crucial. The Adjusted Days Calculator provides a reliable metric for understanding how actual work hours translate into standard workdays. This tool adjusts the number of days based on the actual hours worked, giving a clearer picture of productivity and scheduling effectiveness.
Formula of Adjusted Days Calculator
The formula to calculate Adjusted Days is straightforward:
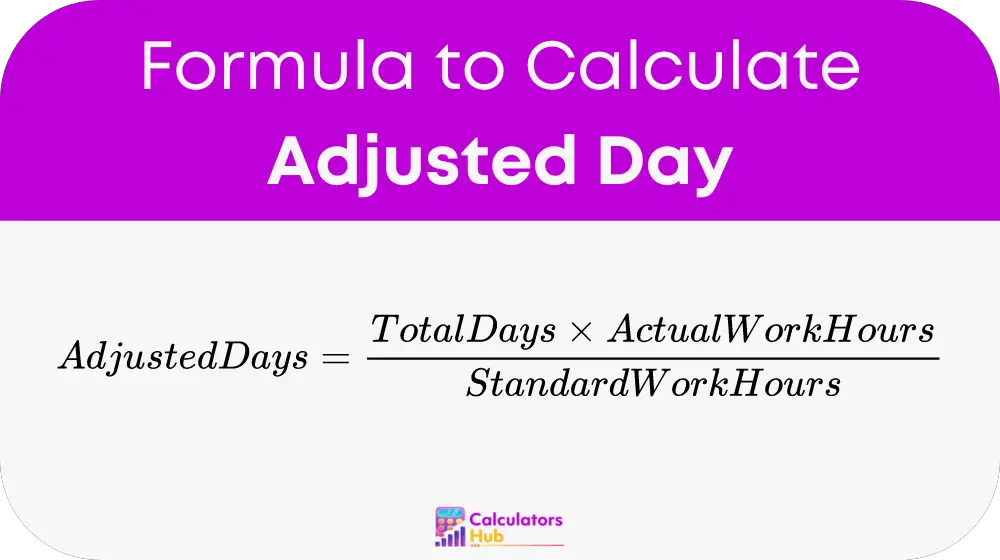
Here's what each term represents:
- Total Days: The total number of days in the period being considered.
- Actual Work Hours: The actual number of hours worked per day, which may include regular hours plus overtime.
- Standard Work Hours: The typical work hours per day as defined by the organization, often assumed to be 8 hours.
Detailed Steps for Calculation
- Determine Total Days: Count the total number of days in the period you are calculating. For example, if calculating for a month, this would be the number of calendar days in that month.
- Identify Actual Work Hours: Calculate the total actual work hours for the period and divide by the number of days to get the average actual work hours per day.
- Determine Standard Work Hours: This is typically set by organizational norms or project requirements, often 8 hours.
- Calculate Adjusted Days: Apply the formula by multiplying the total days by the average actual work hours per day, then divide by the standard work hours per day to get the adjusted days.
Table for General Terms and Useful Conversions
To aid in understanding and utilizing the Adjusted Days Calculator without performing manual calculations each time, here is a table of examples:
| Total Days | Avg. Actual Work Hours/Day | Standard Work Hours/Day | Adjusted Days |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 7 | 8 | 26.25 |
| 30 | 9 | 8 | 33.75 |
| 30 | 10 | 8 | 37.5 |
| 15 | 8 | 8 | 15 |
| 15 | 6 | 8 | 11.25 |
This table exemplifies how variations in work hours affect the adjusted days outcome, providing a quick reference that can be extremely useful for planning and evaluation.
Example of Adjusted Days Calculator
Consider a scenario where a project spanned 20 days in a month, with employees working an average of 9 hours daily, against a standard 8-hour workday. Using our formula:
Adjusted Days = (20 * 9) / 8 = 22.5
This calculation shows that although the calendar period was 20 days, the amount of work done equates to 22.5 standard workdays, highlighting enhanced productivity or overwork.
Most Common FAQs
A1: It helps organizations adjust the actual work performed to a standard scale, facilitating fair assessment and planning of workloads and resources.
A2: Yes, it's adaptable for any work pattern, whether part-time, full-time, or overtime. Making it a versatile tool for various employment scenarios.
A3: Significant discrepancies should prompt a review of work patterns. Possibly adjusting project timelines or employee workloads to better align with actual productivity.