The Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Calculator quantitatively measures resistance in the pulmonary arteries, affecting the heart’s workload during blood pumping through the lungs. Accurate PVR calculation enables better diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of conditions like pulmonary hypertension.
Formula of Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Calculator
The formula for Pulmonary Vascular Resistance is:
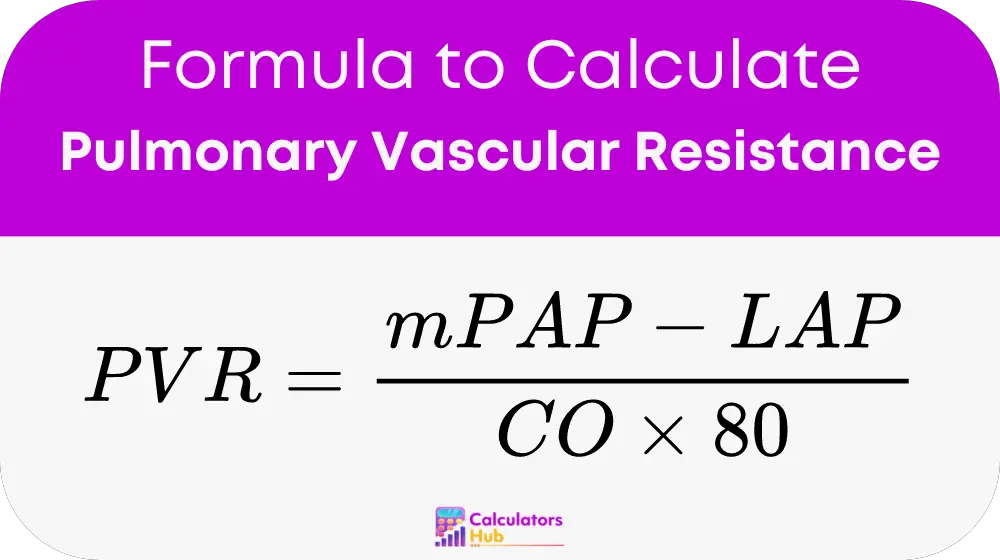
Where:
- PVR is Pulmonary Vascular Resistance in dynes/sec/cm^5,
- mPAP is Mean Pulmonary Artery Pressure in mmHg,
- LAP is Left Atrial Pressure in mmHg,
- CO is Cardiac Output in L/min,
- 80 is a conversion factor for unit consistency.
This formula converts complex clinical measurements into actionable data that guide patient care.
Practical Application
| Condition | PVR Value Range (dynes/sec/cm^5) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 20 – 120 | Normal range for healthy individuals |
| Mild Pulmonary Hypertension | 120 – 240 | Mildly elevated resistance, monitoring recommended |
| Moderate Pulmonary Hypertension | 240 – 360 | Moderate elevation, clinical intervention likely |
| Severe Pulmonary Hypertension | 360 and above | Severely elevated, immediate intervention required |
Example of Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Calculator
For making concepts more clear let us look at an example. For a patient with the following measurements:
- mPAP: 25 mmHg
- LAP: 5 mmHg
- CO: 5 L/min Using the formula: PVR = (25 – 5) / (5 x 80) = 20 / 400 = 0.05 dynes/sec/cm^5 This calculation aids in assessing the patient’s condition and planning treatment.
Most Common FAQs
Typical PVR values range from 20 to 120 dynes/sec/cm^5. Values beyond this suggest pulmonary arterial hypertension.
It helps diagnose pulmonary conditions, monitor treatment efficacy, and predict outcomes.
It should be used as part of a comprehensive assessment, considering other clinical indicators and diagnostic tests.