The Calvert Equation Calculator provides a method for calculating the correct dose of carboplatin based on a patient's glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the target area under the curve (AUC). By inputting these values, healthcare professionals can determine the optimal dosage, improving the likelihood of achieving the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing potential toxicity. The calculator is particularly useful for tailoring treatments to patients with varying kidney function, as the drug's clearance can significantly affect dosing requirements.
Formula of Calvert Equation Calculator
To calculate the dose of carboplatin, the following formula is used:
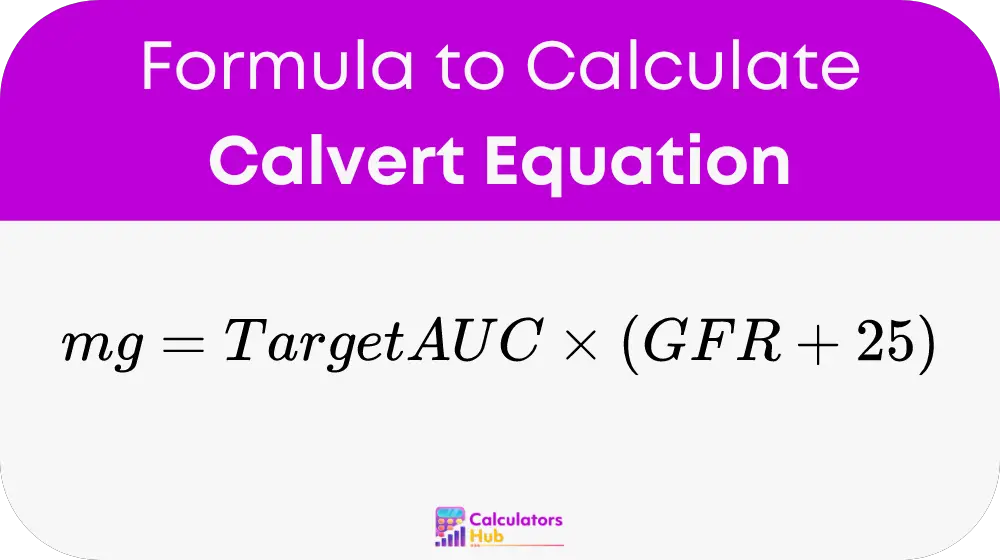
Where:
- Dose (mg) = The total dose of the chemotherapy drug.
- Target AUC = The target area under the curve, which is typically specified by the oncologist (usually between 4 and 6 mg/mL/min for carboplatin).
- GFR = The glomerular filtration rate of the patient, often measured in mL/min. If GFR is not available, creatinine clearance (CrCl) is sometimes used as an estimate.
- 25 = A constant specific to carboplatin, representing non-renal drug clearance.
This formula incorporates the patient's kidney function into the dosing regimen, thereby enhancing the safety and efficacy of the treatment.
Helpful Reference Table
To aid healthcare providers in making quick calculations, here’s a table that outlines common target AUC values and corresponding dose calculations based on different GFR levels. This can serve as a helpful reference for those managing carboplatin dosing without recalculating each time.
| Target AUC (mg/mL/min) | GFR (mL/min) | Dose (mg) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 60 | 340 |
| 4 | 70 | 360 |
| 5 | 50 | 325 |
| 5 | 60 | 350 |
| 6 | 70 | 380 |
| 6 | 80 | 400 |
This table provides quick estimates for healthcare professionals, enabling efficient decision-making regarding carboplatin dosing.
Example of Calvert Equation Calculator
Let’s walk through an example to illustrate how the Calvert Equation Calculator works. Suppose a patient has a GFR of 50 mL/min, and the oncologist specifies a target AUC of 5 mg/mL/min.
Using the formula:
Dose (mg) = 5 × (50 + 25)
Dose (mg) = 5 × 75 = 375 mg
In this scenario, the appropriate dose of carboplatin for the patient would be 375 mg. This calculation demonstrates how the Calvert Equation Calculator can help tailor chemotherapy dosages based on individual patient factors.
Most Common FAQs
Using the Calvert Equation helps ensure that patients receive the correct dose of carboplatin, which is crucial for maximizing treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects. Individualizing the dose based on kidney function is particularly important, as it directly impacts drug clearance and overall safety.
The Calvert Equation is specifically designed for carboplatin dosing. Other chemotherapy drugs may have different pharmacokinetics and dosing requirements, so it is essential to use the appropriate formulas for each specific medication.
GFR should be monitored regularly in patients receiving carboplatin, especially if they have pre-existing kidney conditions or if there are changes in their health status. Regular assessments help ensure that dosing remains accurate and safe throughout treatment.