Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a measure of the amount of oxygen that microorganisms will consume while decomposing organic matter in a water sample. The BOD calculator helps users compute this value efficiently, thereby assessing the level of pollution in the water. It is particularly useful for routine monitoring and ensures that water treatment processes meet environmental standards.
Formula of BOD Calculator
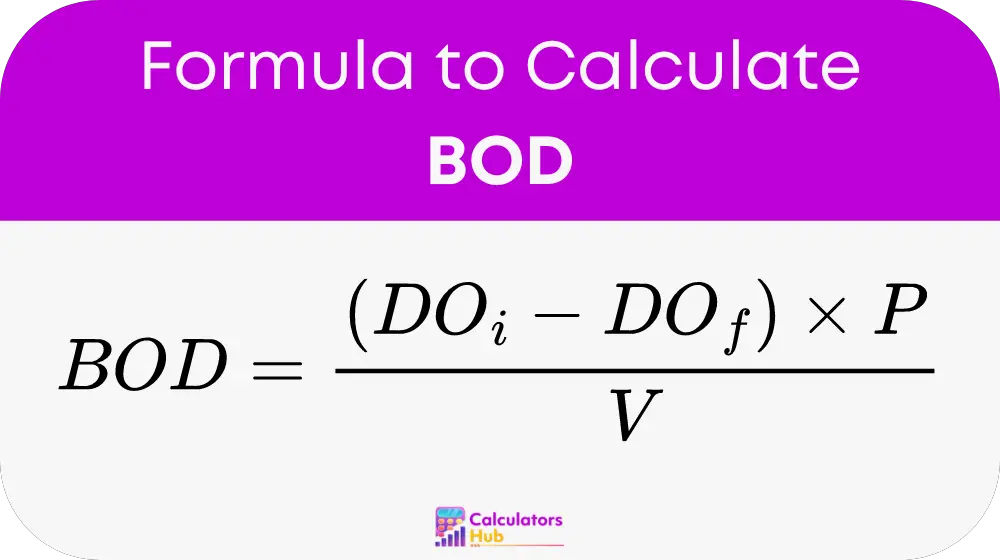
Where:
-
BODis the Biological Oxygen Demand (mg/L). -
DO_iis the initial dissolved oxygen concentration (mg/L). -
DO_fis the final dissolved oxygen concentration (mg/L). -
Pis the sample dilution factor (dimensionless). -
Vis the sample volume (L).
Table for General Terms
To aid in the use of the BOD calculator, here is a table of general terms and typical values:
| Term | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| VV | Sample Volume | 300 mL |
| PP | Dilution Factor | 1:2, 1:5, 1:10 |
| DODO | Dissolved Oxygen Concentrations | 0-12 mg/L |
Example of BOD Calculator
Consider a scenario where the initial dissolved oxygen level is 9 mg/L, and after 5 days it drops to 3 mg/L with a dilution factor of 1:5 in a 300 mL sample. Using the BOD calculator:
BOD = (9−3) × 5 / 0.3=100 mg/L
This calculation shows the water sample has a BOD of 100 mg/L, indicating a moderate level of organic pollution.
Most Common FAQs
Measuring BOD is essential for assessing water quality and determining the effectiveness of wastewater treatment processes.
Common errors include incorrect sample volumes and dilution factors. Always verify input values and calibrate equipment regularly.
Routine BOD testing is recommend at least weekly to monitor treatment efficiency and maintain regulatory compliance.