The Antibiotic Resistance Index (ARI) Calculator is a critical tool used by microbiologists, epidemiologists, and healthcare professionals to measure and quantify the resistance of bacterial populations to various antibiotics. This tool helps in assessing the spread and severity of antibiotic resistance within a community or healthcare setting, providing essential data that can guide public health decisions and antibiotic stewardship programs.
Formula of Antibiotic Resistance Index Calculator
The calculation of the Antibiotic Resistance Index (ARI) involves the following formula:
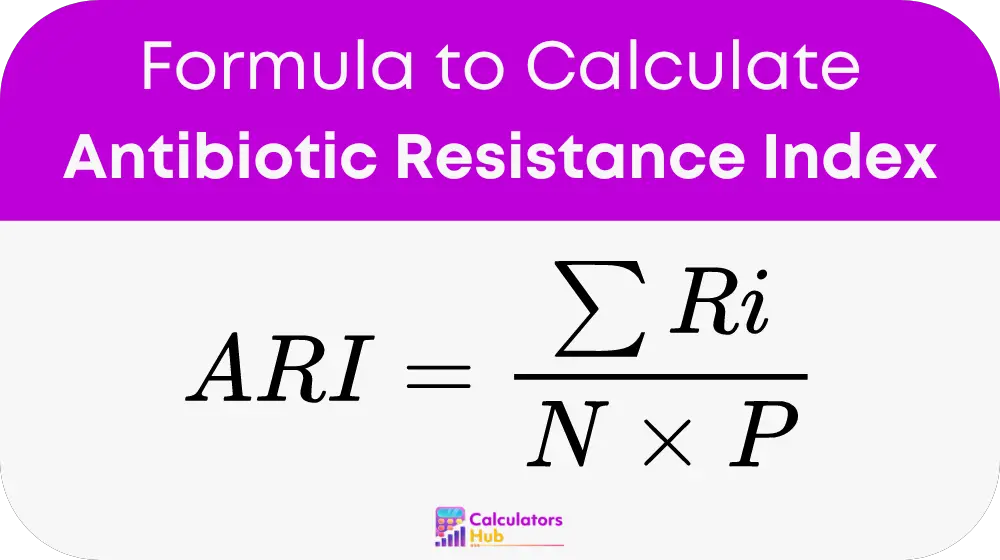
Detailed Explanation
- ARI: Antibiotic Resistance Index, a numerical measure of resistance levels.
- Σ Ri: Sum of the resistance scores of all antibiotics tested.
- N: Total number of antibiotics tested.
- P: Total number of bacterial isolates tested.
Steps for Calculation
- Calculate the resistance score (Ri) for each antibiotic based on susceptibility testing.
- Sum the resistance scores (Σ Ri) for all antibiotics involved in the study.
- Determine the total number of antibiotics (N) and isolates (P) tested.
- Apply the values to the ARI formula to obtain the index value.
General Reference Table
To facilitate a clearer understanding, here’s a table that categorizes potential ARI scores and their implications for public health:
| ARI Score | Resistance Level | Public Health Implication |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 0.2 | Low | Minimal resistance; optimal antibiotic effectiveness |
| 0.21 – 0.5 | Moderate | Growing resistance; caution needed in antibiotic use |
| 0.51 – 0.7 | High | Significant resistance; major concerns for treatment efficacy |
| 0.71 – 1.0 | Very High | Severe resistance; urgent need for alternative treatments and strategies |
Example of Antibiotic Resistance Index Calculator
For instance, consider a study analyzing the resistance of a bacterial population to 5 antibiotics across 100 isolates. Suppose the sum of the resistance scores calculated is 200. Using the ARI formula:
- Σ Ri = 200
- N = 5
- P = 100
Applying the values to the formula:
- ARI = 200 / (5 * 100) = 0.4
This ARI score of 0.4 indicates a moderate level of antibiotic resistance, suggesting the need for monitored antibiotic use and further investigation.
Most Common FAQs
The ARI provides a quantifiable measure of antibiotic resistance in a population, helping healthcare providers understand resistance patterns and tailor antibiotic use policies to combat antimicrobial resistance effectively.
The frequency of ARI calculation should align with ongoing surveillance efforts, typically annually or biannually, to track resistance trends and adjust strategies accordingly.
While ARI primarily measures resistance levels, it indirectly helps predict antibiotic efficacy by indicating which antibiotics are likely to be effective or ineffective against a bacterial population.