ANC is a crucial indicator of a person’s ability to fight off infections. The ANC Count Calculator helps in quickly determining this count by using a simple formula, thereby aiding in rapid decision-making in clinical settings.
Formula of ANC Count Calculator
The formula used by the ANC Count Calculator is straightforward:
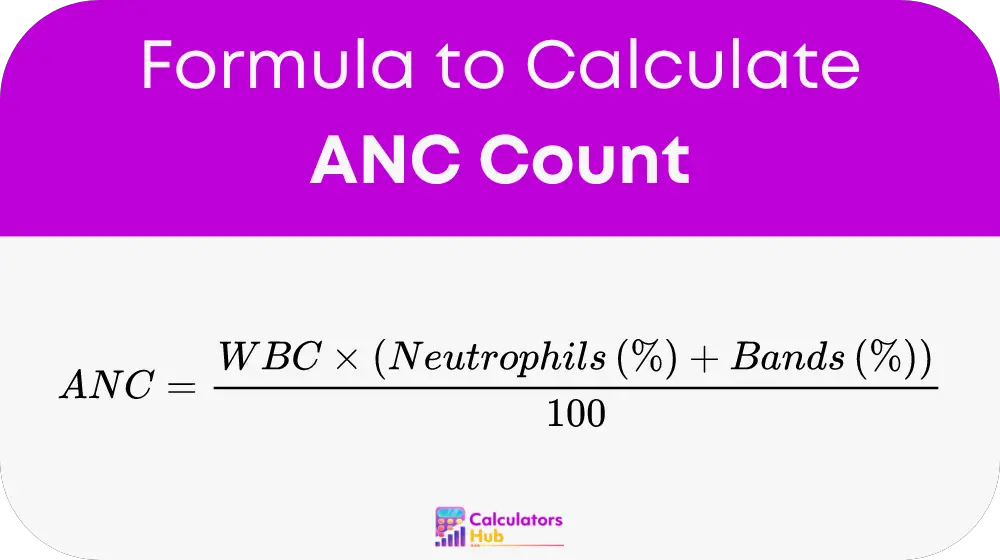
Here’s what each term represents:
- WBC (White Blood Cell count): The total number of white blood cells per unit of blood volume, measured in cells per microliter.
- Neutrophils (%): The percentage of neutrophils in the blood.
- Bands (%): The percentage of band cells (immature neutrophils) in the blood.
Step-by-Step Calculation
To calculate the ANC, follow these steps:
- Convert Percentages to Decimals: Divide the percentage of neutrophils and bands by 100 to convert them into decimal form.
- Add Decimal Values: Sum the decimal values of neutrophils and bands.
- Calculate ANC: Multiply the total WBC count by the sum of the decimal values from step 2. This result gives you the ANC.
Useful Reference Table
Below is a reference table that provides standard WBC count ranges and their corresponding possible ANC values:
| WBC Count (cells/µL) | Neutrophils (%) | Bands (%) | Estimated ANC (cells/µL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5000 | 60 | 3 | 3150 |
| 7500 | 50 | 5 | 4125 |
| 10000 | 70 | 2 | 7200 |
This table helps in quick assessments without the need for detailed calculations every time.
Example of ANC Count Calculator
Let’s consider a patient with the following blood cell counts:
- WBC: 8000 cells/µL
- Neutrophils: 65%
- Bands: 5%
Using our formula, the ANC would be calculated as follows:
ANC = (8000 * (0.65 + 0.05)) / 100 = 5600 cells/µL
This example demonstrates how the calculator simplifies the process of determining the ANC.
Most Common FAQs
A1: ANC is vital for determining a patient’s risk of infection, especially in scenarios involving immunosuppression.
A2: The frequency of ANC monitoring should be determined by a healthcare professional, based on the patient’s health status and treatment plan.