The Allometric Equation Calculator is a specialized tool designed to facilitate the calculation of relationships between biological attributes of organisms. This calculator uses an allometric equation, a type of power law, which helps in predicting how certain characteristics such as metabolic rate or body part size change with variations in the size of an organism.
Formula of Allometric Equation Calculator
The formula used in the Allometric Equation Calculator is:
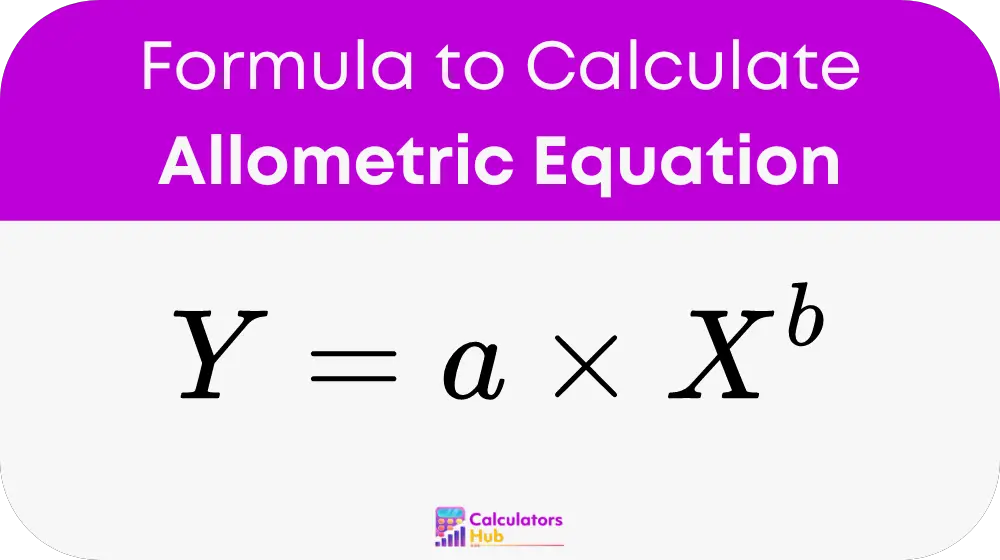
Here:
- Y is the dependent variable, representing characteristics such as body part size or metabolic rate.
- X is the independent variable, typically the overall body size or mass of the organism.
- a is the scaling coefficient, a constant that adjusts the equation for different organisms or conditions.
- b is the scaling exponent, a constant that describes how the dependent variable changes with respect to the independent variable.
Table of Common Allometric Relations
The following table lists some common allometric relationships that are pre-calculated for general use, providing a quick reference without the need for manual calculations:
| Independent Variable (X) | Dependent Variable (Y) | Coefficient (a) | Exponent (b) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Mass (kg) | Metabolic Rate (W) | 70 | 0.75 | Describes how metabolic rate scales with body mass in mammals. |
| Body Mass (kg) | Heart Weight (g) | 4.5 | 0.87 | Shows the relationship between body mass and heart weight. |
| Body Mass (kg) | Brain Weight (g) | 0.12 | 0.67 | Indicates how brain weight scales with body mass among vertebrates. |
Example of Allometric Equation Calculator
Consider a scenario where we want to calculate the metabolic rate of a mammal with a body mass of 30 kg using the allometric equation provided:
Metabolic Rate (W) = 70 * (30^0.75)
By computing, this yields approximately 413 Watts, which represents the energy expenditure of the mammal at rest.
Most Common FAQs
The scaling exponent (b) provides insights into the proportional change in a physiological or morphological trait relative to changes in body size. It is fundamental in understanding growth patterns, evolutionary biology, and ecological dynamics.
While the calculator provides general estimates that are applicable across a wide range of species, specific adjustments might be needed for accurate predictions in uniquely adapted species or under unusual conditions.
Yes, like all models, the allometric equations come with inherent assumptions and simplifications, which can introduce errors. It is advise to use the results as general guidelines and consult more detail data or experts when precise information is need.