The Crop Coefficient Calculator is a useful tool in agriculture and irrigation planning. It helps estimate crop water requirements by calculating the crop coefficient (Kc). The crop coefficient is an essential factor in determining the actual water needs of different crops at various growth stages. By using this calculator, farmers, agronomists, and irrigation specialists can efficiently manage water resources and optimize irrigation schedules to enhance crop yields.
Formula of Crop Coefficient Calculator
To determine the crop coefficient (Kc), the following formula is used:
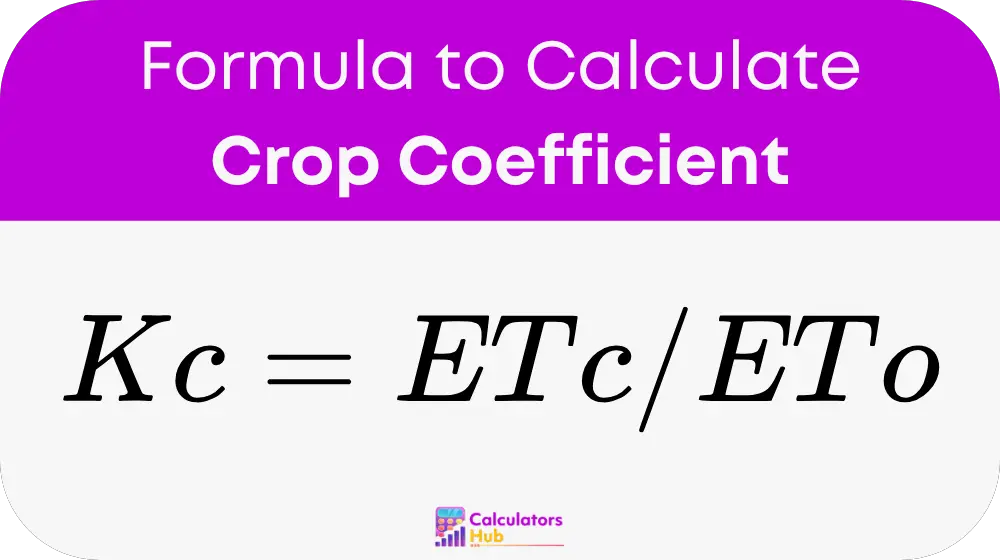
Where:
- Kc is the crop coefficient.
- ETc is the crop evapotranspiration, which is the total amount of water transpired by the crop and evaporated from the soil.
- ETo is the reference evapotranspiration, which represents the water loss from a well-watered, standardized reference crop (such as grass).
The crop coefficient varies depending on the type of crop, growth stage, and climatic conditions.
Crop Coefficient Values by Growth Stage
The crop coefficient changes as the plant grows. The general stages are:
| Growth Stage | Typical Kc Range |
|---|---|
| Initial Stage | 0.3 - 0.5 |
| Development Stage | 0.5 - 0.75 |
| Mid-Season Stage | 0.75 - 1.2 |
| Late-Season Stage | 0.5 - 0.85 |
These values are approximate and depend on crop type, soil moisture, and environmental conditions.
Example of Crop Coefficient Calculator
If the reference evapotranspiration (ETo) is 6 mm/day and the crop evapotranspiration (ETc) is 4.5 mm/day, the crop coefficient (Kc) is calculated as follows:
Kc = 4.5 / 6 = 0.75
This means that the crop in this stage requires 75% of the reference evapotranspiration for proper growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
The crop coefficient helps determine the actual water requirement of crops at different growth stages, allowing for efficient water management and optimized irrigation scheduling.
No, the crop coefficient changes as the plant progresses through its growth stages. It is lower during early growth and higher during peak growth periods.
Factors such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and soil moisture affect evapotranspiration rates, which in turn impact the crop coefficient.