The Drop Out Ratio Calculator helps determine the percentage of individuals who leave or discontinue from a group, program, course, or organization before completing the expected term. This calculator is commonly used in education, training programs, community initiatives, and workforce retention analysis. It serves as a simple but powerful tool to identify how well a program retains its participants.
In education, for example, dropout ratio shows how many students left before finishing a grade or course. Institutions use this ratio to improve student engagement and reduce early withdrawals.
This calculator belongs to the Education Analytics Calculator category. It assists educators, policy makers, and analysts in making data-driven decisions for better program performance.
formula of Drop Out Ratio Calculator
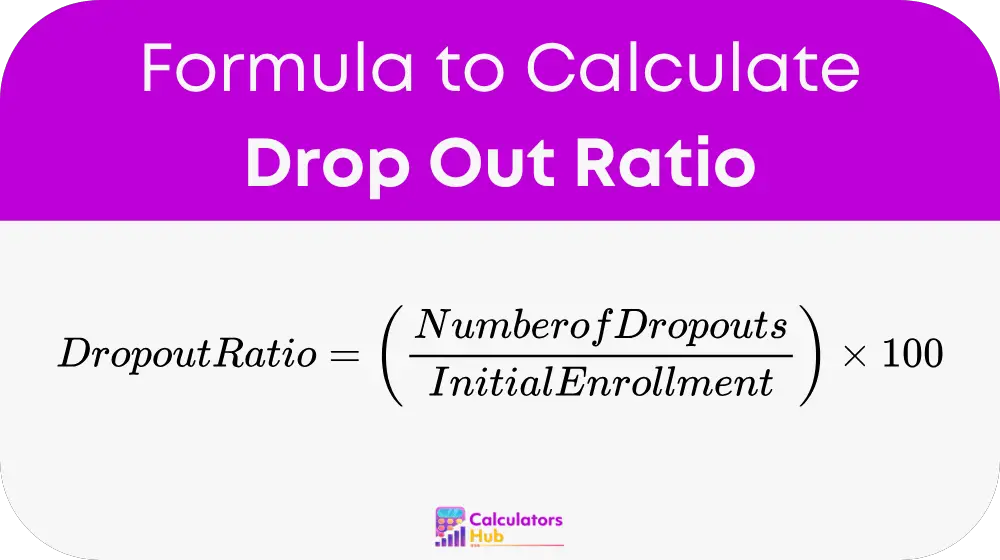
Where:
Dropout Ratio is expressed as a percentage
Number of Dropouts is the count of individuals who left
Initial Enrollment is the starting count of individuals
This formula helps quantify retention issues and is an important metric in analyzing success and consistency in any group-based initiative.
Dropout Ratio Quick Reference Table
This table shows commonly needed dropout ratios without requiring manual calculation:
| Initial Enrollment | Number of Dropouts | Dropout Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 5 | 5.00% |
| 100 | 10 | 10.00% |
| 100 | 25 | 25.00% |
| 100 | 50 | 50.00% |
| 200 | 10 | 5.00% |
| 200 | 20 | 10.00% |
| 200 | 40 | 20.00% |
| 500 | 50 | 10.00% |
| 1000 | 100 | 10.00% |
| 1000 | 250 | 25.00% |
You can use this table for a quick estimate when dealing with standard-sized groups.
Example of Drop Out Ratio Calculator
Let’s say a school started the year with 300 students in Grade 10. At the end of the year, 30 students left without completing.
Apply the formula:
Dropout Ratio = (Number of Dropouts ÷ Initial Enrollment) × 100
Dropout Ratio = (30 ÷ 300) × 100 = 10%
So, the Dropout Ratio is 10%. This means 10% of the students left before completing the year.
Most Common FAQs
A good dropout ratio is usually below 5%. Lower ratios indicate better retention and program success.
Yes, it works in any area where people enter and leave a group—like training programs, clubs, or workforce analysis.
It helps identify problems in retention. High dropout ratios often suggest issues in engagement, support, or environment.