- 二极管电流计算器 有助于确定在二极管上施加一定电压时流过的电流量。这种计算对于设计和分析涉及二极管的电路至关重要,例如 整流器、信号处理和 功率 规 在各种电子设备中。
通过使用此计算器,工程师和学生可以快速计算正向偏置二极管场景中的二极管电流。这简化了二极管性能的分析,并确保了电路中元件的准确选择。
二极管电流计算器公式
用于计算流过二极管的电流的公式基于 肖克利 二极管方程:
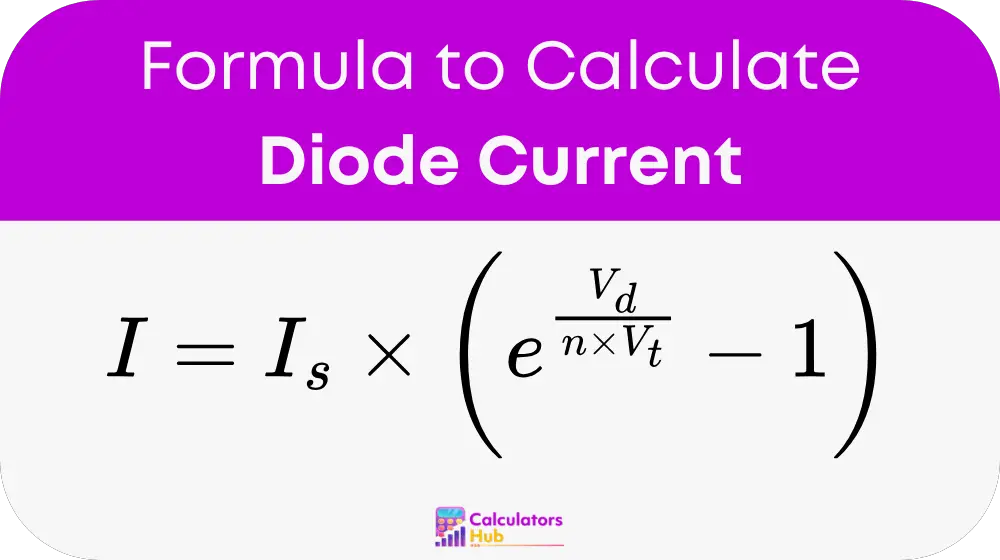
其中:
- I (二极管电流)是流过二极管的电流(以安培为单位)。
- 是 (饱和电流)是二极管反向偏置时的小漏电流(以安培为单位)。
- 电压 (二极管电压)是施加在二极管两端的电压(以伏为单位)。
- n (理想因子)是一个常数(通常在 1 和 2 之间),取决于二极管材料。
- 速度 (热电压)由下式给出 V_t = kT/q,其中:
- k (玻尔兹曼常数)= 1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K
- T (温度单位为开尔文)= 室温通常为 300K
- q (电子电荷)= 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
- 速度 室温下 ≈ 25.85 mV
该方程有助于根据二极管的电压、饱和电流和热特性以及材料特性计算二极管电流。
二极管电流计算的一般术语
下表解释了二极管电流计算中涉及的常用术语:
| 按揭年数 | 图形符号 | 定义 |
|---|---|---|
| 二极管电流 | I | 流过二极管的电流(以安培为单位)。 |
| 饱和电流 | 是 | 二极管反向偏置时的小反向漏电流。 |
| 二极管电压 | 电压 | 施加在二极管两端的电压(以伏特为单位)。 |
| 理想因素 | n | 取决于二极管材料的常数(通常在 1 和 2 之间)。 |
| 热电压 | 速度 | 该电压与温度有关,室温(25.85K)时约为300mV。 |
| 玻尔兹曼常数 | k | 热电压计算中使用的常数:1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K。 |
| 电子电荷 | q | 电子的电荷:1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ C。 |
该表提供了理解和应用二极管电流计算公式的基本定义。
二极管电流计算器示例
例 1:计算室温下的二极管电流
假设我们有一个二极管,其饱和电流 (I_s) 为 10⁻¹² A,施加电压 (V_d) 为 0.7 V,理想因子 (n) 为 1.5。室温 (T = 300 K) 下的热电压为 25.85 mV。
使用二极管电流公式:
I = I_s × (e^(V_d / (n × V_t)) - 1)
代入给定值:
I = 10⁻0.7 × (e^(1.5 / (25.85 × 10 × 1⁻XNUMX)) - XNUMX)
首先计算热电压:
V_t = 25.85 毫伏 = 0.02585 伏
然后:
n × V_t = 1.5 × 0.02585 = 0.038775
V_d / (n × V_t) = 0.7 / 0.038775 = 18.06
e^18.06 ≈ 6.52 × 10⁷
e^18.06 - 1 ≈ 6.52 × 10⁷
我= 10⁻¹²×6.52×10⁷
我≈6.52×10⁻⁵A
因此,二极管电流约为 65.2 μA。
例2:LED二极管电流计算
对于 LED二极管 - I_s = 10⁻¹⁴ A, V_d = 2.1V及 N = 1.2时,室温下的二极管电流可以类似地计算出来。
最常见的常见问题解答
选择二极管时,确保其 饱和电流(I_s) 和 额定电压 符合电路的要求。此外, 理想因子(n) 在当前计算中应考虑准确性,特别是对于更精确的应用。
温度影响 热电压(V_t) 和 饱和电流(I_s),导致二极管电流随温度变化。随着温度升高, V_t增加及 是 通常每 10°C上升.
超过二极管的最大额定电流可能导致 损坏或故障 二极管由于过度 热 或半导体材料击穿。务必确保电流在额定范围内,以免发生电路故障。