A drift velocity calculator is a specialized tool that determines how fast charged particles (typically electrons) move through a conductor when an electric field is applied. Unlike the random thermal motion of electrons, drift velocity measures the slow, net movement in one direction caused by an electric field.
The calculator helps engineers, physicists, and students determine:
- How quickly electrons travel through different materials
- The relationship between current and electron movement
- How material properties affect electrical conductivity
- The efficiency of various conductors for specific applications
Understanding drift velocity is essential for designing efficient electrical systems, selecting appropriate materials for conductors, and analyzing the behavior of electric circuits.
Formula of Drift Velocity Calculator
The drift velocity of charged particles in a conductor can be calculated using the following formula:
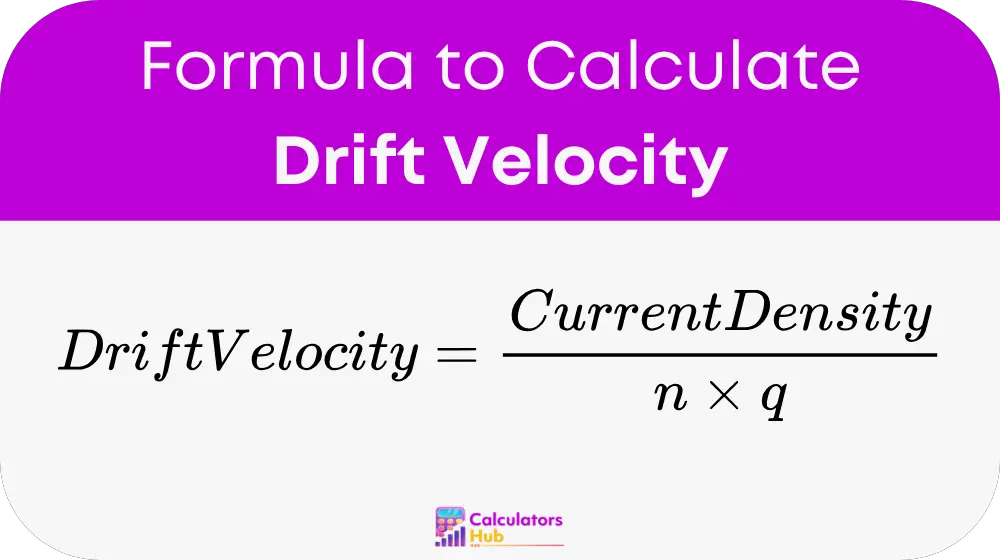
地点:
- Drift Velocity is measured in 米每秒 (M / S)
- Current Density is the electric current per unit cross-sectional area (A/m²)
- n is the number density of charge carriers (number per cubic meter)
- q is the charge of each carrier (库仑)
For electrons, q equals the elementary charge (approximately 1.602 × 10^-19 coulombs).
You can also express this formula in terms of current (I) and cross-sectional area (A):
Drift Velocity = I / (n × q × A)
地点:
- I 是电流,单位为安培 (A)
- A is the cross-sectional area in square meters (m²)
Reference Table for Drift Velocity Values
| 材料 | Typical 载流子密度 (n) per m³ | Typical Drift Velocity at 1 A/mm² |
|---|---|---|
| 铜 | 8.5×10^28 | 2.3 × 10^-5 m/s |
| 铝板 | 6.0×10^28 | 3.2 × 10^-5 m/s |
| 白银 | 5.8×10^28 | 3.3 × 10^-5 m/s |
| 黄金 | 5.9×10^28 | 3.3 × 10^-5 m/s |
| 铁 | 1.7×10^28 | 1.1 × 10^-4 m/s |
| 钨 | 1.3×10^28 | 1.5 × 10^-4 m/s |
| 硅 | 1.0×10^16 | 1.9 × 10^-1 m/s |
| 锗 | 2.4×10^19 | 8.0 × 10^-2 m/s |
Note: These values are approximations and may vary based on temperature, purity, and other factors.
Example of Drift Velocity Calculator
Let's calculate the drift velocity of electrons in a copper wire:
鉴于:
- Current (I) = 2 amperes (A)
- Wire diameter = 1.5 millimeters (mm)
- Number density of electrons in copper (n) = 8.5 × 10^28 per cubic meter
- Charge of an electron (q) = 1.602 × 10^-19 coulombs
Step 1: Calculate the cross-sectional area of the wire.
A = π × (diameter/2)² = π × (0.00075)² = 1.767 × 10^-6 m²
Step 2: Calculate the current density.
Current Density = I/A = 2/1.767 × 10^-6 = 1.132 × 10^6 A/m²
Step 3: Calculate the drift velocity using our formula.
Drift Velocity = Current Density / (n × q)
Drift Velocity = 1.132 × 10^6 / (8.5 × 10^28 × 1.602 × 10^-19)
= 8.31 × 10^-5 m/s
This means the electrons in this copper wire move at approximately 0.0000831 meters per second, or about 0.3 millimeters per hour, when carrying a current of 2 amperes.
最常见的常见问题解答
While electrons move slowly through conductors (typically millimeters per hour), electrical signals travel near the speed of light. This is because the electric field moves through the wire almost instantly, causing all electrons to begin moving simultaneously throughout the entire circuit.
Higher temperatures increase the random thermal motion of electrons, which creates more collisions and resistance. This typically reduces drift velocity as electrons have a harder 次 moving in one direction.
Yes, when there's no current flowing through a conductor, the drift velocity is zero because there's no net movement of charge carriers in any particular direction.