- 库存天数计算器 帮助企业确定 average number of days inventory remains in stock before being sold. This metric is essential for understanding inventory turnover, operational 效率, and cash 流 管理.
主要 benefits of calculating days in inventory:
- 帮助企业 optimize stock levels and reduce holding costs.
- Assists in identifying slow-moving inventory that may need discounts or promotions.
- 提供深入了解 供应链效率 and demand forecasting.
- 帮助公司 compare inventory performance across different periods or competitors.
较低的 days in inventory value means faster turnover, while a higher value may indicate overstocking or weak sales performance.
Formula for Days In Inventory Calculator
The standard formula for calculating days in inventory 是:
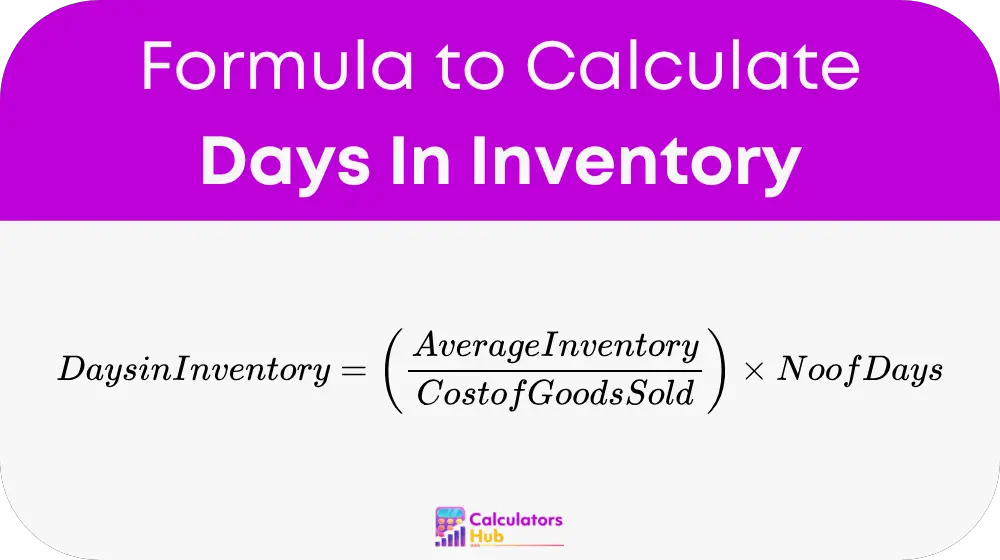
地点:
- 平均库存 = (Beginning Inventory + Ending Inventory) / 2
- 销货成本(COGS) = Total cost of goods sold during the period
- 天数 = 周期 长度 (e.g., 30 for a month, 365 for a year)
Days In Inventory Reference Table
下表提供 common industry benchmarks for days in inventory:
| 产业应用 | 平均库存天数 |
|---|---|
| Retail / 零售 | 30 – 60天 |
| 汽车 | 50 – 90天 |
| 消费品 | 40 – 80天 |
| 技术 | 20 – 50天 |
| 制造 | 60 – 120天 |
These figures vary based on industry trends, demand, and supply chain efficiency.
Example of Days In Inventory Calculator
Scenario: Calculating Days In Inventory for a Retail Business
A retail store has the following data for the year:
- 期初库存: $50,000
- 期末库存: $40,000
- 销售成本 (COGS): $300,000
- Period Length: 为期365天
步骤1:计算平均库存
(50,000 + 40,000) / 2 = $45,000
第 2 步:应用公式
(45,000 / 300,000)×365 = 54.75天
The business holds inventory for an average of 54.75 days before selling it.
最常见的常见问题解答
较低的 days in inventory ratio is usually better because it indicates fast-moving stock and efficient operations. However, the ideal value depends on the 行业中的应用: 和 商业模式.
Businesses can improve this metric by enhancing demand forecasting, streamlining supply chains, and reducing excess stock. 策略包括 即时 (JIT) 库存管理 can help optimize stock levels.
Yes, a high value may suggest slow sales, overstocking, or supply chain inefficiencies。 可能导致 higher storage costs and product obsolescence.