The Design Effect Calculator helps statisticians, researchers, and survey analysts estimate the impact of cluster sampling on variance. In survey research, clustering can lead to a design effect that influences the precision of estimates, requiring adjustments to sample sizes. This tool is essential for ensuring accurate statistical inferences and improving survey reliability.
Formula of Design Effect Calculator
The Design Effect is calculated using the following formula:
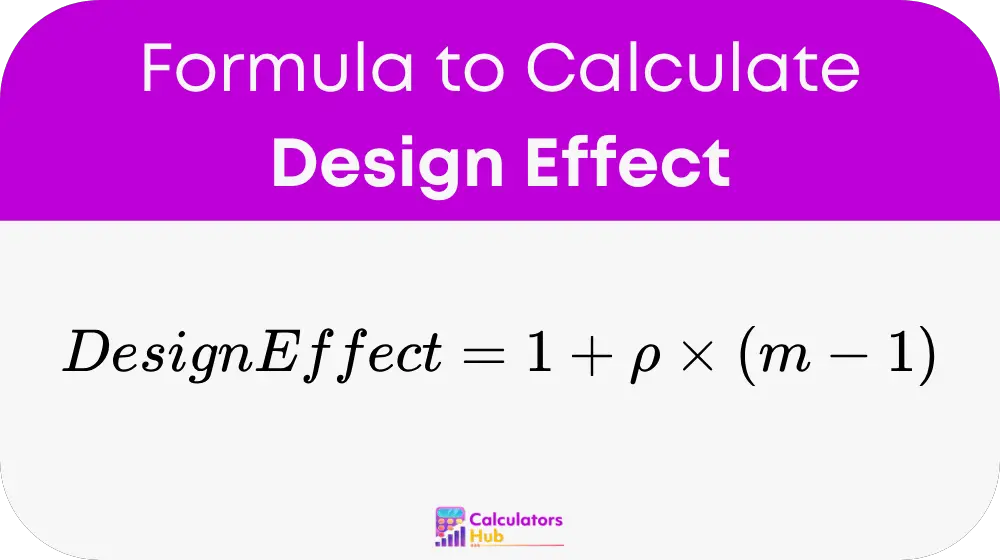
where:
- ρ (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient) represents the similarity of individuals within clusters.
- m (Cluster Size) is the average number of subjects per cluster.
This formula accounts for the increase in variance due to cluster sampling and helps researchers determine appropriate sample sizes.
Design Effect Reference Table
This table provides estimated design effects for different intraclass correlation coefficients (ρ) and cluster sizes (m) to assist researchers in determining sampling adjustments.
| Intraclass Correlation (ρ) | Cluster Size (m) | Design Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 0.01 | 5 | 1.04 |
| 0.05 | 10 | 1.45 |
| 0.10 | 20 | 2.90 |
| 0.20 | 30 | 5.80 |
| 0.30 | 50 | 15.70 |
These values help researchers understand how clustering affects survey precision.
Example of Design Effect Calculator
A researcher is conducting a survey using a cluster sampling method with an intraclass correlation coefficient (ρ) of 0.10 and an average cluster size (m) of 20. Using the formula:
Design Effect = 1 + 0.10 × (20 - 1)
= 1 + 0.10 × 19
= 1 + 1.90 = 2.90
This means the effective sample size is reduced by a factor of 2.90 due to clustering, requiring an adjustment in sample size calculations.
Most Common FAQs
The design effect accounts for the impact of clustering on sample variance, ensuring that researchers adjust sample sizes correctly for accurate statistical inferences.
A higher intraclass correlation (ρ) increases the design effect, meaning greater adjustments are need to account for clustering in survey sampling.
Yes, minimizing cluster size and increasing sample diversity can help reduce the design effect, improving survey precision and efficiency.