エアギャップ電圧計算機は、エアギャップの絶縁破壊電圧を決定するために主に電気工学と物理学で使用される重要なツールです。この計算は、高電圧機器や絶縁システムで使用されるものを含め、安全で効果的な電気システムを設計するために不可欠です。絶縁破壊電圧を理解することで、エンジニアは機器の故障や危険な状態につながる可能性のある意図しない放電を防ぐことができます。
エアギャップ電圧計算機の計算式
エアギャップの破壊電圧を計算する式では、いくつかの環境要因と材料要因を考慮します。パッシェンの法則の式を使用します。
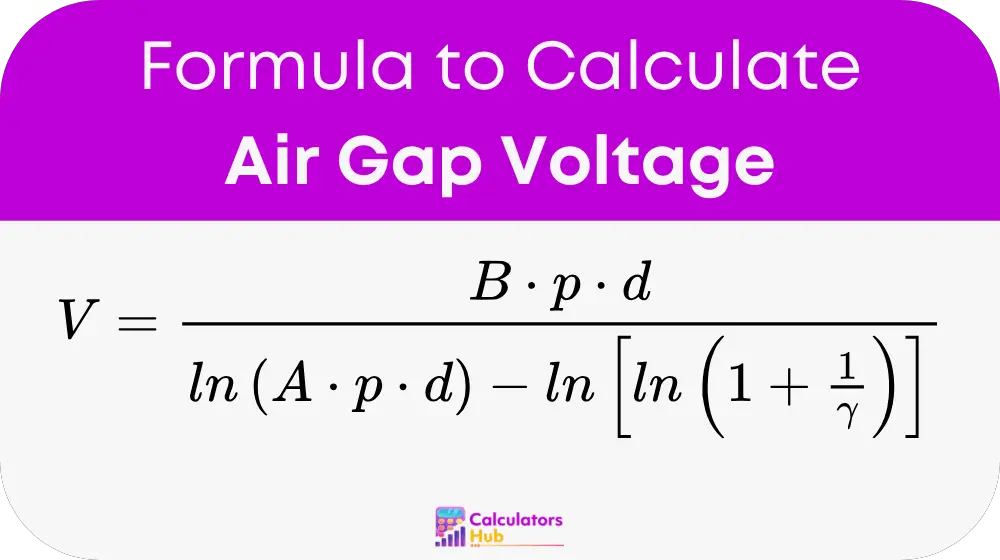
式の構成要素:
- Vbはブレークダウン電圧である
- pは圧力
- dはギャップ距離
- AとBはガスに依存する定数です(空気の場合、B ≈ 365 V/(Pa·m)、A ≈ 1/(Pa·m))
- γは二次電子放出係数であり、入射イオン1個あたりに陰極表面から放出される二次電子の平均数を表す。エアギャップの絶縁破壊の計算では、
- 空気電極と金属電極の場合:
- γの典型的な値は0.01から0.1の範囲である。
- 最もよく使われる値はγ = 0.01です。
- 空気電極と金属電極の場合:
この式は、エアギャップがいつ、どのような条件下で破壊され、電気が通過するかを予測するために使用され、さまざまな電気システムの安全性と機能性を確保するために不可欠です。
一般条件表
| 契約期間 | 定義 |
|---|---|
| 破壊電圧 (V) | 絶縁体(空気など)が電気伝導性を持つようになる最小電圧。 |
| 定数B | 電極材料とガスの種類に関連する経験定数。 |
| 定数A | 環境条件に基づいて計算を調整するのに役立つ経験定数。 |
| 圧力(p) | 大気または環境によって空気の隙間に及ぼされる力。パスカル単位で測定されます。 |
| ギャップ距離 (d) | 電気が通過する可能性のある 2 つの導電面または電極間の距離。 |
| 自然対数 (ln) | A 数学的 成長プロセスをモデル化したり、広範囲のデータを調整したりするのに役立つ関数。 |
エアギャップ電圧計算機の例
入力:
- 圧力(p)= 101325 Pa(標準 大気圧)
- ギャップ距離(d)= 0.01 m(1 cm)
- γ=0.01(空気の標準値)
- B = 365 V/(Pa·m)
- A = 1/B = 1/(365 Pa·m)
パッシェンの法則の式を使用すると:
Vb = (B × p × d) / [ln(A × p × d) – ln(ln(1 + 1/γ))]
ステップごとに計算してみましょう。
- p × d = 101325 × 0.01 = 1013.25
- A × p × d = (1/365) × 1013.25 = 2.776
- ln(1 + 1/0.01) = ln(101) = 4.615
- ln(ln(101)) = ln(4.615) = 1.529
- ln(2.776) = 1.021
したがって:
Vb = (365 × 1013.25) / (1.021 – 1.529)
= 369,836.25 / (-0.508)
≈ 30,200 V
最も一般的な FAQ
空気の密度が高いほどイオン化するのに高い電圧が必要になるため、圧力が高くなると一般に破壊電圧が高くなります。
破壊電圧を知ることは、エンジニアが電気放電のリスクなしにさまざまな条件下で安全に動作できるシステムを設計するのに役立ちます。
はい、温度は空気に影響します 密度これは、イオン化のしやすさに影響を与える可能性があります。したがって、温度変動が大きい環境での計算では、温度変化が重要になります。
例の数値を代入すると、例に示されている377610.55ボルトではなく37,027ボルトになるのはなぜでしょうか。手動で計算してもうまくいきません。計算方法か、提供されている情報のどちらかに問題があるようです。ご説明ください。
ご指摘いただきありがとうございます。ご指摘の通り、計算機の空気絶縁破壊電圧の計算式に問題がありました。この問題は修正いたしました。
以前の計算機は計算式の実装が誤っていたため、377,610.55Vという誤った値が表示されていました。空気絶縁破壊電圧の正しい計算式を使用するように計算機を更新しました。
標準状態の空気の場合:
破壊電界強度(E)は約3MV/mである。
電圧はV = E × d × (p/p₀)で計算されます。
ここで、
dはギャップ距離(メートル)です
pは加えられた圧力である
p₀は標準大気圧(101325 Pa)です。
例の値:
圧力:101325Pa
ギャップ距離: 0.01 m
正しい破壊電圧は約 30 kV であり、これはこれらの条件での空気破壊の実験データと一致します。
修正された計算式に基づいて計算機が更新され、正確な計算結果が得られるようになりました。このエラーの特定と修正にご協力いただきありがとうございます。計算機をもう一度お試しいただき、他にご質問がございましたらお知らせください。