The Equivalent Noise Temperature Calculator is a helpful tool that calculates the noise temperature of a system or device based on its noise factor. This value shows how much extra noise the system adds when compared to an ideal system at a standard temperature. It’s mostly used in radio, satellite, and wireless communication systems, where noise can affect signal clarity.
Using this calculator saves fois and reduces errors by quickly converting noise factor or noise figure into temperature. It’s useful for engineers and technicians working on low-noise amplifiers, antennas, or other RF systems where performance is highly sensitive to noise.
formula of Equivalent Noise Temperature Calculator
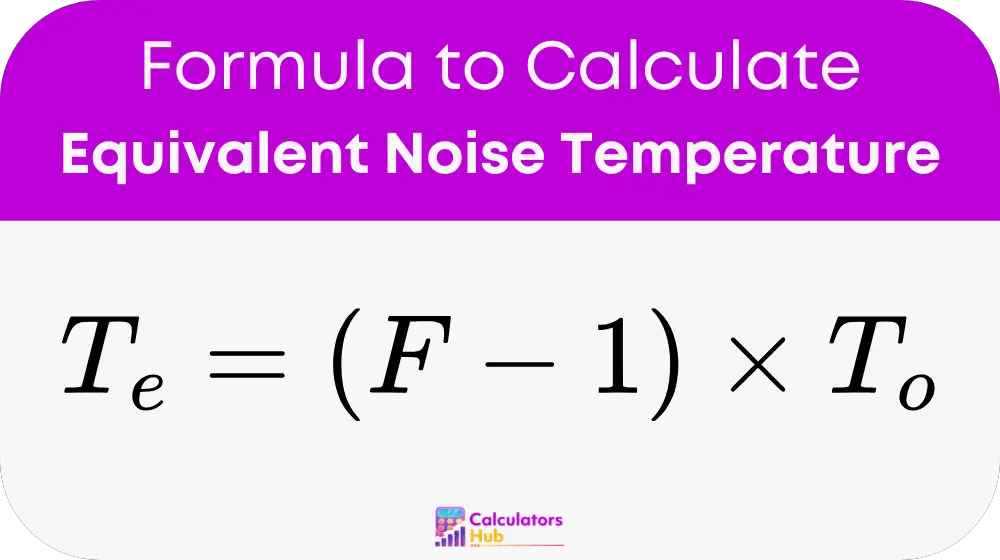
Où :
Tₑ = equivalent noise temperature (kelvin)
F = noise factor (unitless)
T₀ = standard reference temperature = 290 K
If the noise figure is given in decibels (NF), first convert it to noise factor:
F = 10^(NF / 10)
This formula helps engineers see how much noise a system contributes in terms of temperature. It simplifies the comparison between different components by expressing noise in a physical, measurable unit.
Tableau de référence utile
The table below shows estimated equivalent noise temperatures for common noise figures. This can help users skip manual calculations and make quick comparisons.
| Figure de bruit (dB) | Noise Factor (F) | Equivalent Noise Temperature (K) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.122 | 35.4 |
| 1.0 | 1.259 | 75.1 |
| 2.0 | 1.585 | 170.0 |
| 3.0 | 1.995 | 289.6 |
| 5.0 | 3.162 | 631.0 |
| 10.0 | 10.000 | 2,610.0 |
Note: Values use T₀ = 290 K and F = 10^(NF / 10).
This quick lookup table is especially useful during RF system design or when evaluating amplifier chains in communication systems.
Example of Equivalent Noise Temperature Calculator
Imagine you have a device with a noise figure of 3 dB. To find the equivalent noise temperature:
Step 1: Convert the noise figure to noise factor
F = 10^(3 / 10) = 1.995
Étape 2 : Utilisez la formule
Tₑ = (1.995 − 1) × 290
Tₑ = 0.995 × 290 = 288.55 K
So, the equivalent noise temperature is approximately 288.55 kelvin. This shows how much thermal noise is add by the device.
FAQ les plus courantes
It’s a way to describe the noise a system adds in terms of temperature. A higher value means more noise and lower performance in sensitive systems like radios or satellites.
Yes, just convert the dB value to a noise factor first using the formula F = 10^(NF / 10), then use the main equation to get the noise temperature.
This is a standard use in engineering because it represents room temperature (about 17°C). It helps in comparing different systems fairly.