The Cohesive Energy Calculator is a vital tool for understanding the stability and bonding strength within a solid or crystalline material. Cohesive energy quantifies the energy required to separate a material into its individual atoms or molecules, providing critical insights into the material's structural integrity and physical properties. This tool is particularly useful in materials science, solid-state physics, and chemistry, where precise energy calculations help in predicting material behavior and designing new compounds. It belongs to the category of materials property calculators, aiding researchers and engineers in analyzing and comparing different materials.
Formula of Cohesive Energy Calculator
Cohesive energy is calculated using the formula:
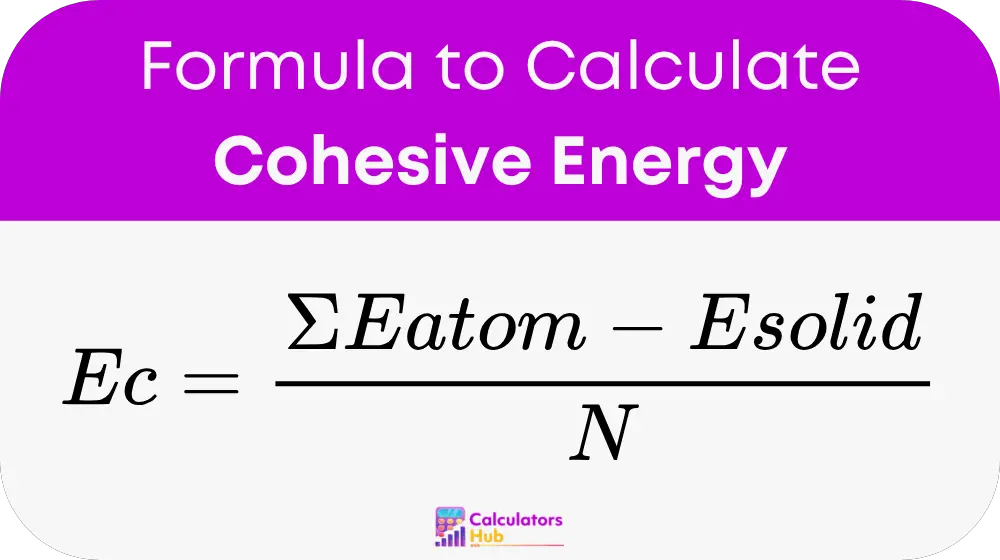
Where:
- Ec is the cohesive energy per atom or molecule.
- Σ Eatom is the total energy of all free atoms or molecules in the unit cell.
- Esolid is the total energy of the solid or crystal structure.
- N is the number of atoms or molecules in the unit cell.
Detailed Formulas for Variables:
Total Energy of Free Atoms or Molecules (Σ Eatom):
Σ Eatom = Eatom × N
Where:
- Eatom is the energy of a single free atom or molecule.
- N is the number of atoms or molecules in the unit cell.
Total Energy of the Solid (Esolid):
Esolid represents the measured or calculated energy of the solid structure. This value is typically determined using computational methods like density functional theory (DFT) or experimental data from spectroscopy or calorimetry.
Cohesive Energy (Ec):
Substitute the values of Σ Eatom, Esolid, and N into the cohesive energy formula to calculate Ec.
Pre-Calculated Table for Cohesive Energy of Common Materials
Below is a reference table showing the cohesive energies of some commonly studied materials. This helps users understand typical values without performing detailed calculations:Material Cohesive Energy (eV/atom) Interpretation Sodium (Na) 1.13 Low bonding strength Copper (Cu) 3.49 Moderate metallic bonding Diamond (C) 7.37 Very high bonding strength Silicon (Si) 4.63 Strong covalent bonding Iron (Fe) 4.28 Moderate metallic bonding Magnesium Oxide (MgO) 10.3 Extremely strong ionic bonding
This table is particularly useful for benchmarking and comparing the cohesive energies of different materials.
Example of Cohesive Energy Calculator
Let’s calculate the cohesive energy of a hypothetical crystal:
- The unit cell contains 4 atoms (N = 4).
- The energy of a single free atom (Eatom) is 5 eV.
- The total energy of the solid (Esolid) is -15 eV.
Step 1: Calculate Total Energy of Free Atoms (Σ Eatom)
Σ Eatom = Eatom × N
Σ Eatom = 5 × 4 = 20 eV
Step 2: Use the Cohesive Energy Formula
Ec = (Σ Eatom - Esolid) / N
Ec = (20 - (-15)) / 4 = (20 + 15) / 4 = 35 / 4 = 8.75 eV/atom
Thus, the cohesive energy is 8.75 eV per atom, indicating strong bonding within the material.
Most Common FAQs
Cohesive energy helps determine the stability, strength, and melting point of a material. Materials with higher cohesive energy generally have stronger bonds and greater thermal stability.
Cohesive energy is typically measured using computational methods like density functional theory (DFT) or experimentally through calorimetry and spectroscopy techniques.
No, cohesive energy is always a positive value. It represents the energy required to break the bonds within a material, so a negative value would not make physical sense.