The extinction coefficient (ε) is a critical parameter used to quantify the concentration of DNA in a solution, measured at a wavelength of 260 nm. This coefficient helps in determining how much light DNA absorbs at this wavelength, which is directly proportional to its concentration. The DNA Extinction Coefficient Calculator provides a straightforward method to compute this coefficient, ensuring that researchers can obtain reliable measurements for their experiments and studies.
Formula of DNA Extinction Coefficient Calculator
To calculate the DNA extinction coefficient, use the following formula:
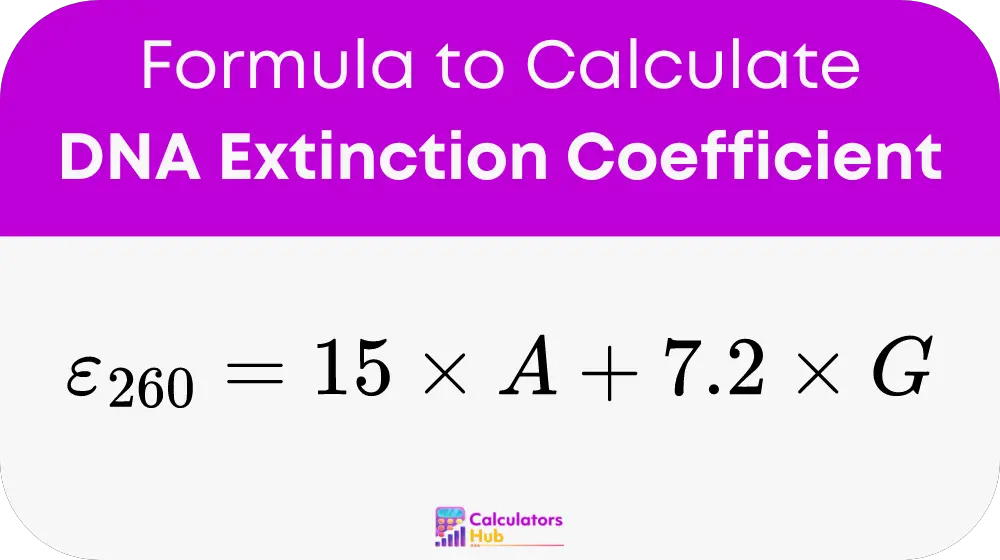
Where:
- A represents the number of adenine residues in the DNA sequence.
- G denotes the number of guanine residues.
This formula allows for the accurate calculation of DNA concentration by accounting for the specific absorption characteristics of adenine and guanine.
Table for General Use
For convenience, below is a table that includes common DNA sequences alongside their calculated extinction coefficients:
| DNA Sequence | Extinction Coefficient (ε_260) |
|---|---|
| AGCT | Computed Value |
| CGTA | Computed Value |
| TCGA | Computed Value |
This table serves as a quick reference to avoid manual calculations for frequently used sequences.
Example of DNA Extinction Coefficient Calculator
Consider a DNA sequence consisting of 10 adenine residues and 5 guanine residues. Using the DNA Extinction Coefficient Calculator:
- ε_260 = 15 * 10 + 7.2 * 5 = 150 + 36 = 186
This result indicates the extinction coefficient for this particular DNA sequence, essential for determining its concentration in a solution.
Most Common FAQs
A: The extinction coefficient measures how much light a DNA sample absorbs at 260 nm. It is crucial for accurately assessing DNA concentration and purity, important in research and clinical settings.
A: You can determine the number of each nucleotide by analyzing the DNA sequence directly or using software tools that count nucleotide occurrences.
A: Always double-check the DNA sequence input for accuracy and confirm the calculations using standard samples for comparison.